Fig. 4. Interactions between socioeconomic status and genetic components that affect white matter integrity.
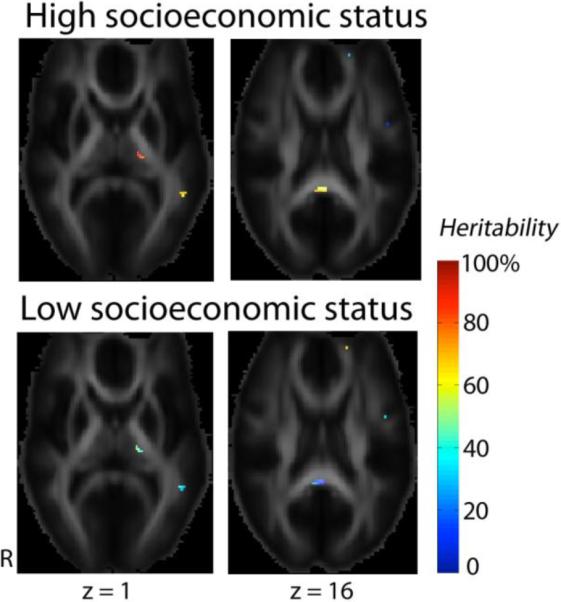
Socioeconomic status was evaluated using the socioeconomic index (SEI, range = 0–100). To show the contrast in FA heritability between subjects with higher versus lower socioecnomic status, we used the 75th percentile (SEI = 83.8) and the 25th percentile of SEI (SEI = 39.7) to represent the higher and the lower socioecnomic groups. In the thalamus, and the middle temporal gyrus on the left (z = 1), and the callosal splenium (z = 16), genetic contributions to the overall variation of FA were higher in the higher socioeconomic group. However, for some small regions in the anterior corona radiata (z = 16), the genetic variance proportion is higher in the lower socioeconomic group. The main effect of SEI on FA was not significant.
