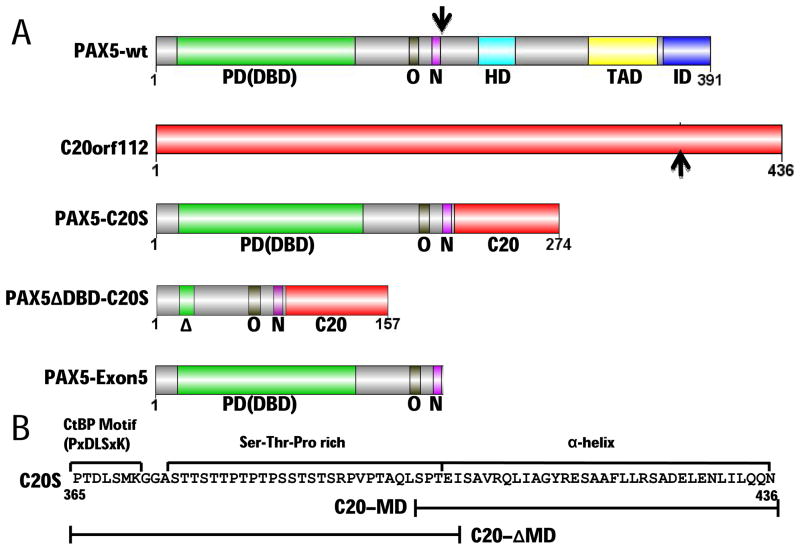
Figure 1. Structural determinants of PAX5-C20orf112 oncogenic fusion protein.
(A) Domains of PAX5 (Cobaleda et al., 2007), C20orf112, PAX5-C20S, PAX5ΔDBD-C20S with the paired DBD deleted, and PAX5-Exon5 (encoded by PAX5 exons 1–5, the portion of PAX5 in PAX5-C20S). The PAX5 DNA-binding domain [PD (DBD)], an octapeptide motif bound by Groucho-family co-repressors (O), and a nuclear localization sequence (N) are included in PAX5-C20S while its partial homeodomain (HD), activation domain (TAD), and inhibitory domain (ID) are not. Black arrows indicate points of fusion. (B) Analysis of C20orf112 sequence in PAX5-C20S reveals three regions that may contribute to DN activity: a CtBP binding motif (P×DLS×K), a serine-threonine-proline (Ser-Thr-Pro)-rich region, and a putative α-helical region. Constructs that contain bracketed parts of C20S are YFP-PAX5-C20-MD that fuses only the α-helical region, and YFP-PAX5-C20ΔMD that fuses only the P×DLS×K motif and the Ser-Thr-Pro rich region.