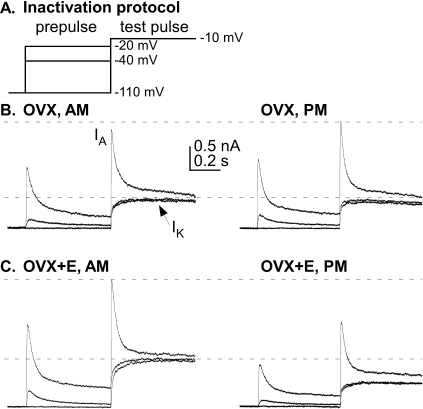
FIG. 1.
GnRH neurons from OVX+E mice but not from OVX mice exhibited a diurnal change in voltage-gated potassium currents. A) A voltage clamp protocol was used to identify voltage-gated potassium currents in GnRH neurons; for clarity, only three prepulse potentials (−110, −40, and −20 mV) are shown. Most of the 500 msec step to −100 mV for removal of inactivation from the A-type channel was omitted. Prepulses and test pulses shown were both 500 msec in duration. B) Representative traces of total potassium current illustrate two components: a fast transient current (IA) and a sustained current (IK) from GnRH neurons from OVX mice, recorded during negative feedback, morning hours (left), and during positive feedback, evening hours (right). The short duration current peak at the beginning of the −40 mV prepulse is the activation of IA, followed by its inactivation during the remainder of the prepulse, allowing measurement of isolated IK during the test pulse. C) Representative traces are shown from GnRH neurons from OVX+E mice recorded during morning hours (left) and evening hours (right).