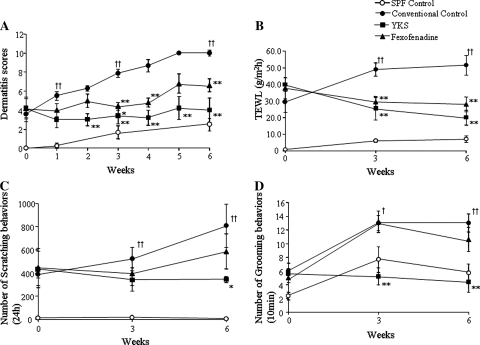
Fig. 1.
The effects of YKS and fexofenadine on dermatitis score (a), TEWL (b), the numbers of scratching behaviors (c) and grooming behaviors (d) for AD-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. a The skin lesions of the conventional control group were aggravated as time goes on. Both the YKS- and the fexofenadine-treated groups significantly inhibited the aggravation of skin lesions in NC/Nga mice from 3 weeks after the start of the experiments. The dermatitis score of the SPF control group was not more than a minor increase. b The TEWL of the conventional control group was increased as time goes on. The YKS- and the fexofenadine-treated groups significantly inhibited the increase of TEWL compared with the conventional control mice from 3 weeks. The TEWL of the SPF group, which had no skin lesions, was not increased. c Scratching behaviors of the conventional control and the fexofenadine-treated groups increased as time goes on. The YKS-treated group significantly decreased the scratching behaviors compared with the conventional control group after 6 weeks. The scratching behaviors of the SPF group were not increased. d Grooming behaviors of the conventional control group and also the fexofenadine-treated group were increased under social isolated conditions. The YKS-treated group significantly decreased the grooming behaviors compared with the conventional control mice from 3 weeks. The grooming behaviors of the SPF group increased under social isolated conditions. SPF control: unfilled circle, conventional control: filled circle, YKS: filled square, fexofenadine: filled triangle. Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 5–6). † p < 0.05, †† p < 0.01 vsersu SPF control, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus conventional control, one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni/Dunn test