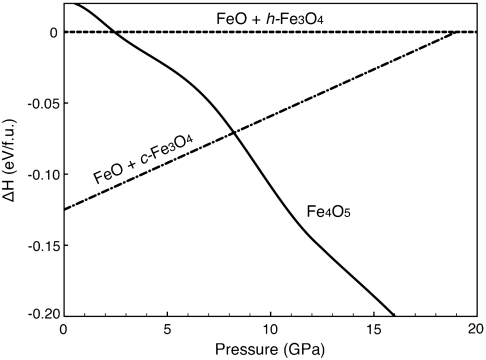
Fig. 4.
Enthalpies of Fe4O5 and of the plausible breakdown oxides FeO and h-Fe3O4. To examine the relative stability of Fe4O5 with respect to its possible breakdown products (FeO and Fe3O4 in the ambient and high-pressure structures), the enthalpy differences, ΔHc = H(Fe4O5) - [H(FeO) + H(c-Fe3O4)] and ΔHh = H(Fe4O5) - [H(FeO) + H(h-Fe3O4)], were calculated as a function of pressure. The solid, dashed, and dot-dashed lines represent the enthalpies of Fe4O5, ΔHh (the reference), and ΔHc, respectively. ΔHc is extracted from the literature (15). The Fe4O5 structure is favored over the sum of breakdown products at 10 GPa.