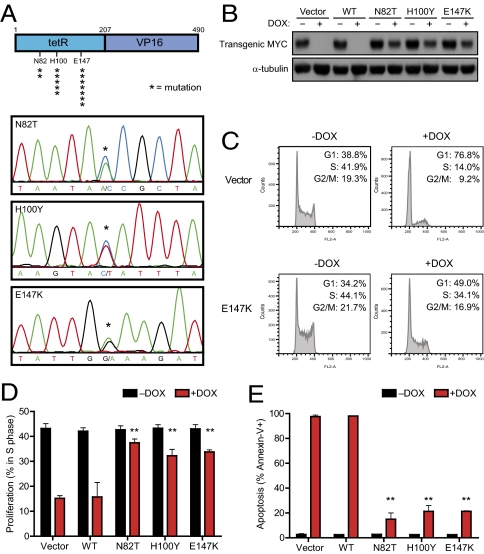
Fig. 3.
Transgenic MYC is reactivated owing to mutations in the tTA protein. (A) Schematic of the tTA protein (asterisks indicate the position and frequency of mutated amino acids) and example chromatograms for the N82T, H100Y, and E147K mutations. (B) Mutant tTAs cloned from recurring lymphomas are insensitive to DOX. A MYC lymphoma line was stably infected with empty vector, wildtype tTA (WT), or mutant tTAs (N82T, H100Y, E147K). Cells were then treated with DOX and analyzed for (B) expression of tTA-dependent transgenic MYC by Western blot (24 h DOX), (C and D) cell cycle status by propidium iodide staining (48 h DOX), or (E) apoptosis rate by Annexin-V staining (5 d DOX). Mean values of a minimum of three independent experiments are shown with SDs where applicable. **P < 0.01, paired t test.