Figure 2.
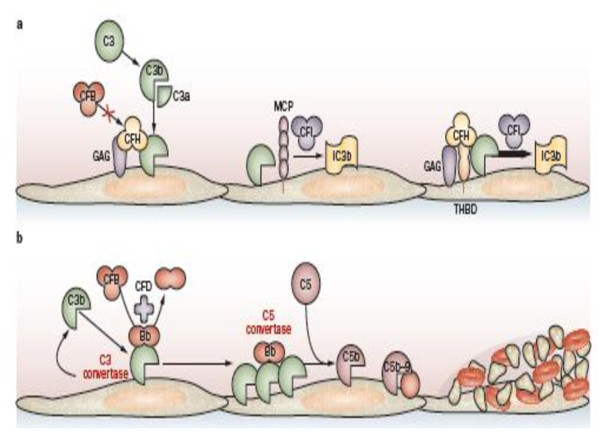
Regulated and deregulated activation of the alternative complement pathway. Figure and comments reproduced from Zuber et al [131]. a) CFH competes with CFB to bind C3b, which hampers the generation of C3 convertase. CFH binds to glycosaminoglycans on the endothelial surface and factors, such as MCP, can act as a cofactor for the CFI-mediated cleavage of C3b to generate iC3b (inactivated C3b). THBD binds to C3b and CFH and might accelerate the CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b. b) Uncontrolled activation of the alternative complement pathway leads to the generation of the membrane-attack complex (C5b-9) through the actions of CFB, CFD and through the generation of C3 convertase and C5 convertase. The resulting injury and activation of endothelial cells initiates a microangiopathic thrombotic process. CFH: factor H; CFI: factor I; CFB: factor B; CFD: factor D; MCP: membrane cofactor protein; THBD: thrombomodulin.
