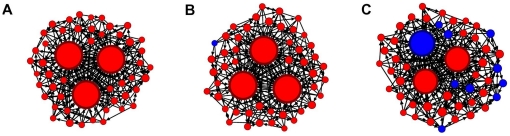
Figure 3. Examples of popularity-based networks.
A) Uniform popularity network; B) Popularity network with a single rule-breaking individual; C) Popularity network with 20% of individuals that did not follow this convention. While the simulations were not spatially explicit, the size of the individuals in a network is proportional to that individual's popularity (in-degree centrality). Even though the individuals that used rule-breaking behavior (identified by their blue color) had social success comparable to the convention-abiding individuals, the emergent properties of the system changed: with more individuals not playing by the rules, the group became more decentralized.