Figure 1.
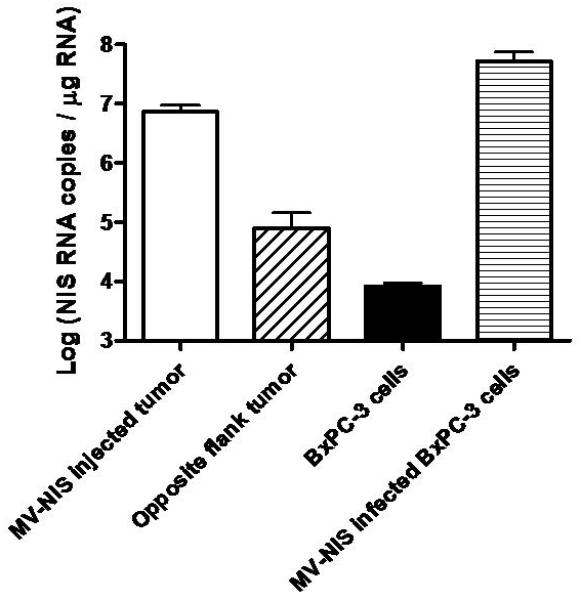
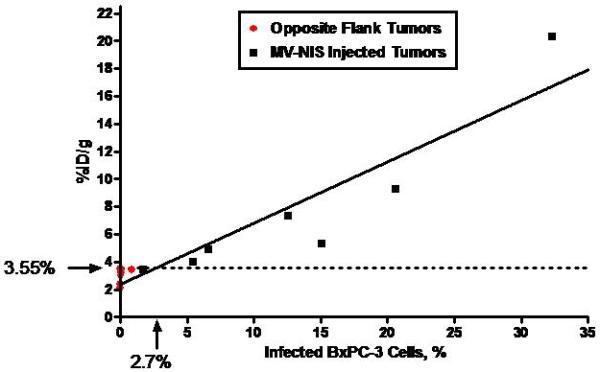
A, Human NIS RNA Levels after Infection with MV-NIS. Tumor homogenates were created from subcutaneous tumors in nude mice (7 MV-NIS–injected tumors and 7 noninjected tumors from the opposite flank). Cultured BxPC-3 cells were optimally infected with MV-NIS. RNA levels were measured by qRT-PCR. The level of NIS RNA/μg in opposite flank tumors and uninfected BxPC-3 cells in vitro was not significantly different. NIS RNA/μg in MV-NIS injected tumors was significantly different than the level in opposite flank tumors (p < 0.01 by t-test). B, Linear regression of 123I uptake (%ID/g) in infected and uninfected BxPC-3 subcutaneous dual flank tumors (n = 7 mice) versus percent infected BxPC-3 cells (as calculated by RNA yield). The dotted line shows the detection sensitivity threshold value (3.55 %ID/g, 1.5 times y-intercept of the regression line) (r2 of linear regression = 0.872, p < 0.001). This corresponded to 2.7% infected tumor cells. %ID/g denotes percent injected dose per gram; MV-NIS, measles virus expressing human NIS; NIS, sodium iodide symporter; qRT-PCR, quantitative, real-time, reverse transcriptase, polymerase chain reaction.
