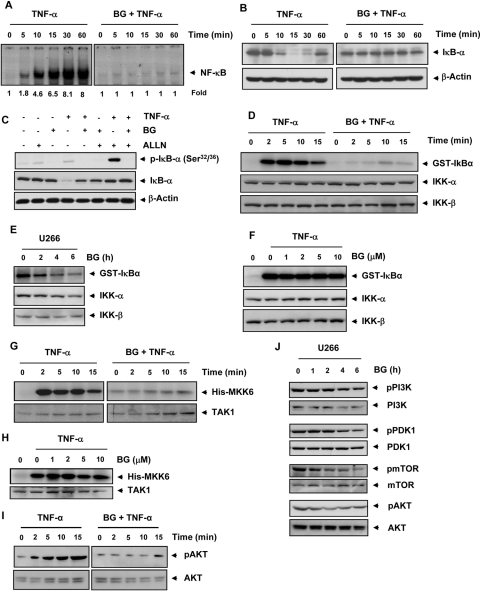
Fig. 2.
Bharangin suppresses TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation via inhibition of IKK activation. A, KBM-5 cells were preincubated with 5 μM bharangin for 6 h and treated with 0.1 nM TNF-α for the indicated times. Nuclear extracts of the cells were analyzed for NF-κB activation using EMSA. The fold activation of NF-κB is indicated at the bottom. B, Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic extracts of KBM-5 cells for IκBα. C, bharangin inhibits TNF-α-induced IκBα phosphorylation. KBM-5 cells were treated with 5 μM bharangin for 6 h, incubated with 50 μg/ml N-acetyl-leucyl-leucyl-norleucinal (ALLN) for 30 min and treated with 0.1 nM TNF-α for 10 min. Cytoplasmic extracts of the cells were analyzed using Western blotting with a phosphorylated IκBα antibody (Ser32/Ser36). The same membrane was reprobed with IκBα. D, bharangin inhibits TNF-α-induced IKK activation. KBM-5 cells were pretreated with 5 μM bharangin for 6 h and then treated with 1 nM TNF-α for the indicated times. Whole-cell extracts of the cells were immunoprecipitated with an antibody against IKK-α and analyzed using an immune complex kinase assay. The effect of treatment with bharangin on IKK protein expression was determined using Western blot analysis with anti-IKK-α and anti-IKK-β antibodies. E, effect of bharangin on constitutive IKK activation in U266 cells. Cells were treated with 5 μM bharangin for the indicated times, and whole-cell extracts of the cells were used in an IKK assay. F, direct effect of treatment with bharangin on TNF-α-induced IKK activation. Whole-cell extracts of KBM-5 cells treated with 1 nM TNF-α were immunoprecipitated with an IKK-α antibody. The immunoprecipitated complex was incubated with bharangin at the indicated concentrations, and an immunocomplex kinase assay was performed. G, effect of bharangin on TNF-α-induced TAK1 activation. KBM-5 cells were preincubated with bharangin (5 μM) for 6 h and then treated with TNF-α (1 nM) for the indicated times. The protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with an antibody against TAK1 and analyzed by an immune complex kinase assay. H, bharangin does not directly affect TAK1 activity. The protein extract prepared from TNF-α treated KBM-5 cells were immunoprecipitated with an anti-TAK1 and the immunocomplex kinase assay was performed in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of bharangin. I, effect of bharangin on TNF-α-induced AKT activation. KBM-5 cells were incubated with 5 μM bharangin for 6 h and then treated with 1 nM TNF-α for the indicated times. Whole-cell extracts of the cells were prepared and analyzed using Western blotting with a phospho-specific AKT antibody. AKT was used as an internal control. J, bharangin inhibits constitutive activation of PI3K, PDK1, mTOR, and AKT in U266 cells. Cells were treated with bharangin (5 μM) for the indicated time. The whole-cell extracts of control and treated cells were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against pPI3K, pPDK1, pmTOR, and pAKT. The unphosphorylated protein was used as an internal control. BG, bharangin; GST, glutathione transferase.