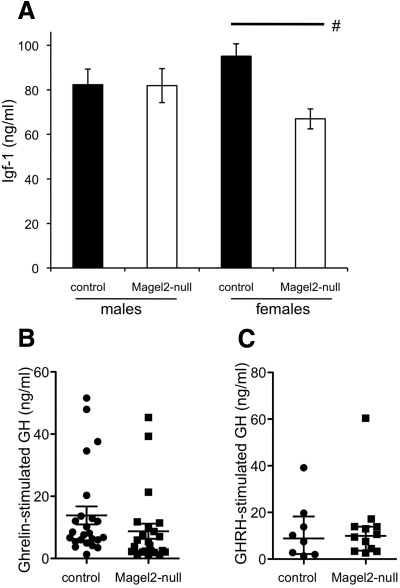
Fig. 5.
Analysis of the GH pathway. A, Serum Igf-I levels were determined as a long-term indicator of GH axis function. Values represent the mean ± sem; n = 5–8 per group. Black bars represent control, and white bars represent Magel2-null. Magel2-null male mice had Igf-I levels similar to those of control littermates, whereas Magel2-null female mice had reduced Igf-I (Student's t test comparing control with Magel2-null, #, P = 0.002). B, Stimulated GH levels were measured after ghrelin injection. Symbols represent individual female mice [control (circles) and Magel2-null (squares)]. The error bars indicate the median and interquartile range. Median levels of ghrelin-stimulated GH were reduced in the Magel2-null mice compared with control (nonparametric Mann-Whitney test, U = 170, P = 0.02; n = 23–24 per group). C, Stimulated GH levels were measured after GHRH injection. Symbols represent individual female mice [control (circles) and Magel2-null (squares)]. The error bars indicate the median and interquartile range. There was no difference between genotypes in GHRH-stimulated GH levels (n = 8–12 per group).