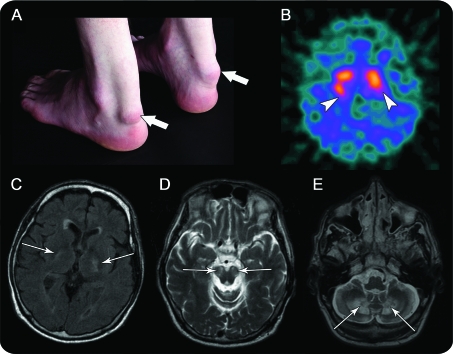
Figure. Clinical and radiologic signs.
(A) Bilateral tendon xanthomas (arrows). (B) I-123-Ioflupane (I-123 FP-CIT) SPECT: reduced bilateral, asymmetric putaminal uptake (arrowheads). MRI (arrows): diffuse volume loss with signal abnormality, (C) in the globus pallidus, internal capsules on axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, (D) cerebral peduncles, substantia nigra, and (E) extensive white matter involvement of the cerebellar hemispheres including dentate nuclei on axial T2-weighted imaging.