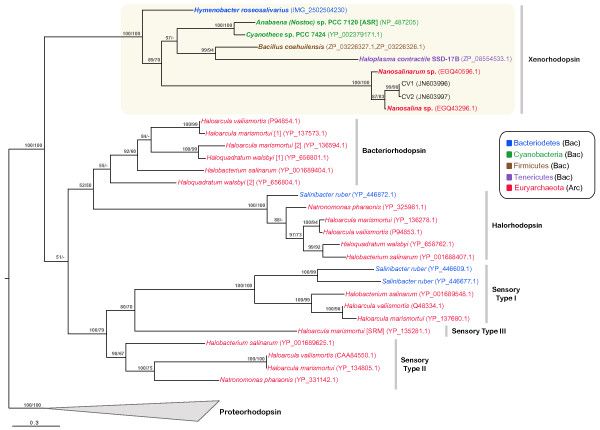
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of microbial rhodopsin proteins showing diversity of functional classes. Tree is based on a total of 34 sequences (205 amino acid positions) using maximum likelihood and Bayesian inference methods. Numbers at nodes represent posterior probablities inferred by MrBayes (first value) and maximum likelihood bootstrap values using RaxML (second value). Only values greater than 50% are shown. GenBank accession numbers are shown in parentheses for each protein except H. roseosalivarus (IMG-ER database gene object ID) [22]. Sequences CV1 and CV2 were recovered by PCR amplification of environmental DNA from a solar saltern in Chula Vista, California, USA, using Nanohaloarchaeal-specific xenorhodopsin primers (see Additional File 1).