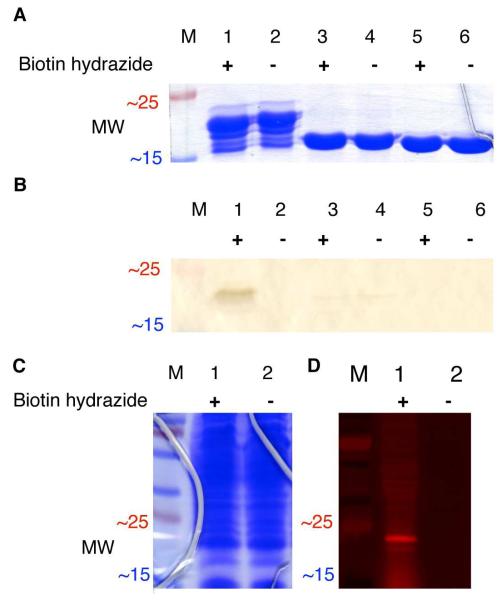
Figure 3.
(A) SDS-PAGE of the purified 53-lysozyme fusion protein (22.3 kDa in lanes 1-2), the fully proteolyzed 53-lysozyme fusion protein (19.2 kDa in lanes 3-4), and wild-type lysozyme (18.6 kDa in lanes 5-6). Each sample was either treated (+) or untreated (−) with biotin hydrazide (1 mM) for 1 h at room temperature before electrophoresis. (B) Western blot analysis for biotin hydrazide labeling the purified 53-lysozyme fusion protein. The protein gel and Western blot, excerpted for clarity here, are shown in full in Figure S2 in Supporting Information. (C) SDS-PAGE of the 53-lysozyme fusion protein in crude E. coli lysates, either treated (+) or untreated (−) with 1 mM rhodamine B hydrazide before separation by SDS-PAGE. (D) The protein lysate shown in C was then transferred electrophoretically to nitrocellulose, and imaged by fluorescence scanning. “M” indicates molecular weight standards.