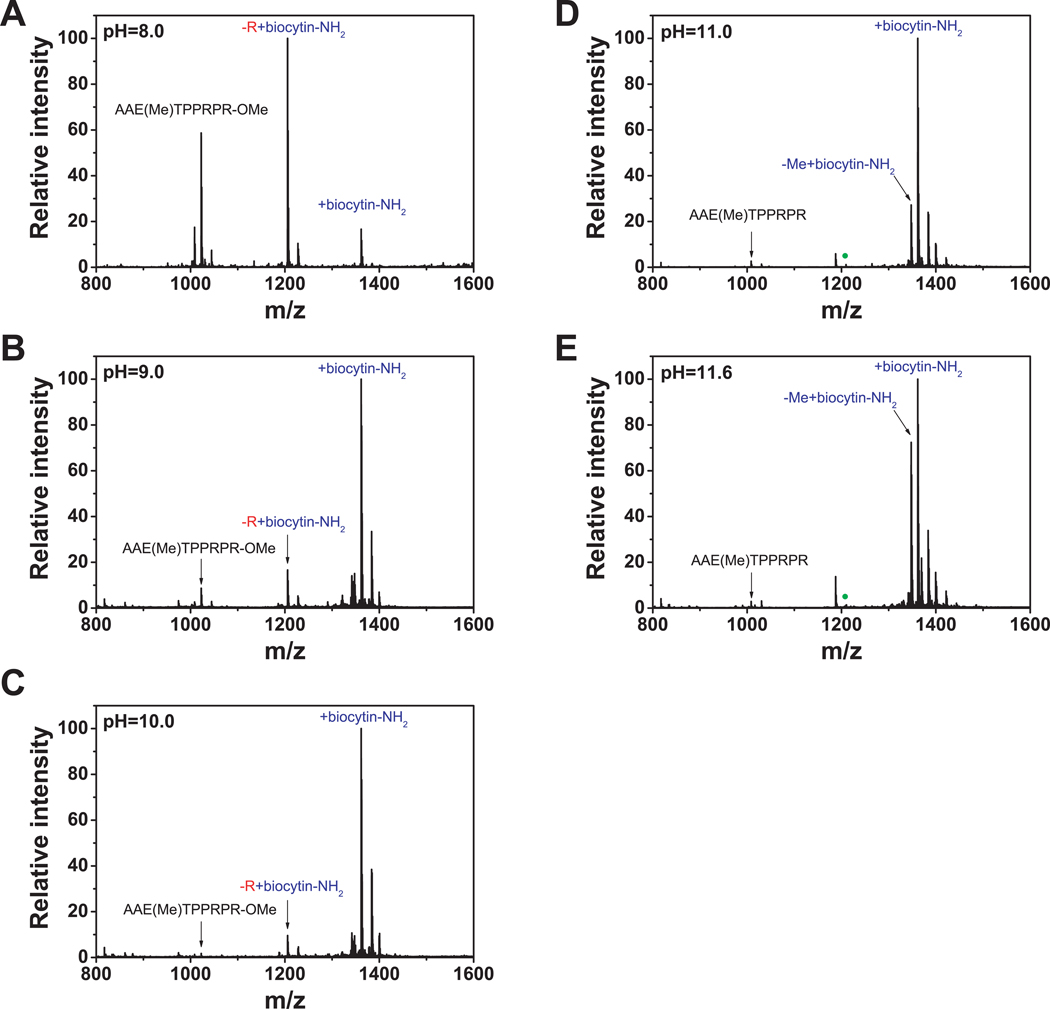
Figure 2. CPY-catalyzed C-terminal modifications are determined by the pH used during labeling.
(A, B, C) The products of CPY-mediated biotinylation were determined using a model peptide, AAETPPRPR, at pHs 8.0, 9.0 and 10.0, and the products were detected by MALDI-TOF-MS.
(D, E) CPY-mediated biotinylation at pHs 11.0 and 11.6 does not result in removal of the C-terminal amino acid. Negligible unmodified peptide was detected, indicating that C-terminal labeling with CPY is highly efficient under these reaction conditions. The green solid circles in (D) and (E) correspond to the position of the biocytinamide-modified peptide missing the C-terminal arginine, which was detected in (A), (B), and (C), but not in (D) and (E).