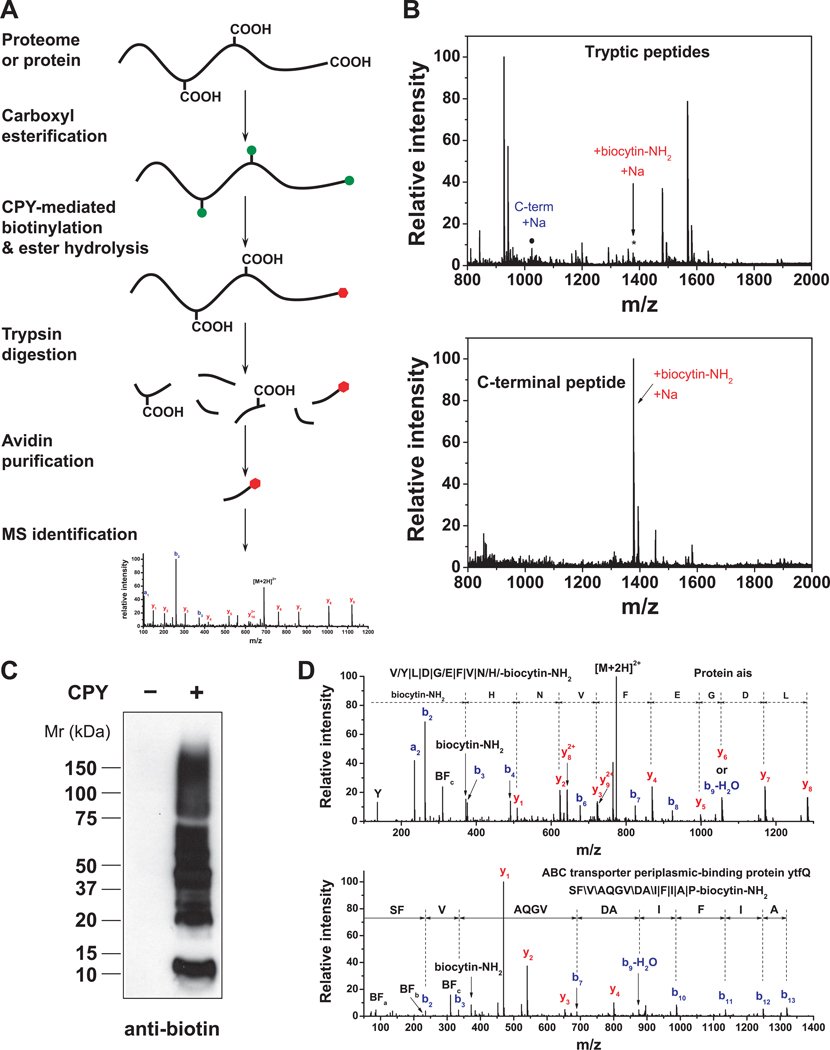
Figure 4. Selective isolation of C-terminal peptides using ProC-TEL.
(A) ProC-TEL strategy for the isolation and identification of C-terminal peptides. Protein carboxyl groups (side chains and C-terminus) are first modified by methyl esterification (green circles). The C-termini are then biotinylated by CPY through the addition of a biotin-containing nucleophile at protein C-termini and methyl esters at the side chains of Glu and Asp are hydrolyzed at high pH at the same time. The biotinylated proteins are digested and the C-terminal peptides with affinity biotin tags (red hexagons) are isolated by avidin affinity chromatography for MS analysis.
(B) Isolation of the C-terminal peptide from a protein using ProC-TEL. After CPY labeling of BSA with biocytinamide and trypsinolysis, numerous tryptic peptides are detected by MALDI-TOF MS (top panel), including the biotinylated C-terminal peptide (asterisk). Following purification of peptides on monomeric avidin agarose, the biotinylated C-terminal peptide is readily detected, while the other unmodified peptides are almost completely removed (bottom panel).
(C) CPY-mediated labeling of proteins in E. coli lysates detected by an anti-biotin Western blotting.
(D) MS/MS spectra of representative C-terminal peptides identified from E. coli lysates using the ProC-TEL approach. The peptide sequence and modification is shown in the spectra and the b-ions and y-ions are labeled. The symbols, \, / and |, represent b-ions, y-ions, and both b-ions and y-ions, respectively. MS/MS spectra for the C-terminal peptide from Protein ais (top panel) and the neo-C-terminal peptide from the ABC transporter ytfQ (bottom panel) are shown. In the MS/MS spectra, three characteristic biotin fragment ions, BFa, BFb, BFc, and biocytinamide ion (biocytin-NH2) are detected for the C-terminal biotinylated peptides.