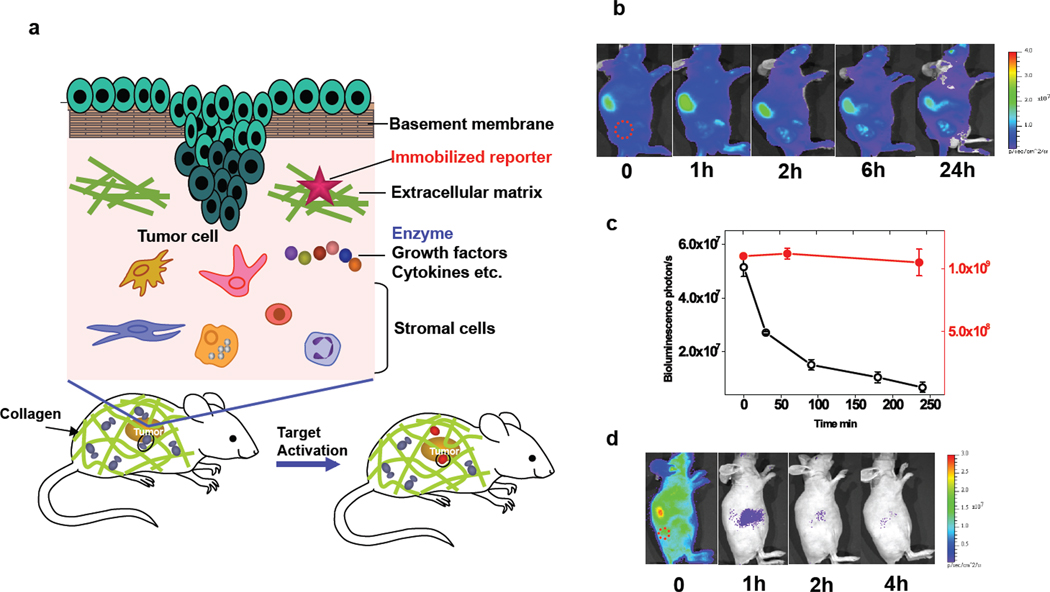
Fig. 1.
A reporter immobilization strategy for in vivo imaging. (a) Schematic of reporter immobilization over the body through binding ubiquitous collagens for imaging the extracellular microenvironment. (b) In vivo bioluminescence imaging of CB-Luc, a fusion reporter of Luc8-535 with CNA35 in nude mice with HT1080 tumor xenografts (marked by a red circle). The reporter protein (10 pmol) was injected via the tail vein (acquisition time, 1 s; 10 µg coelenterazine). The liver showed the highest bioluminescence emission, and the biodistribution of the reporter activity in tissues at 24 h post-injection is shown in Supplementary Fig. 1. (c) Plot of the bioluminescence emission in the whole body (red dot; right y-axis) and in blood (black open circle; left y-axis) at various post-injection time points. (d) Fast clearance of non-immobilized Luc8-535 from the circulation after injection into nude mice with HT1080 tumor xenografts (red circle).