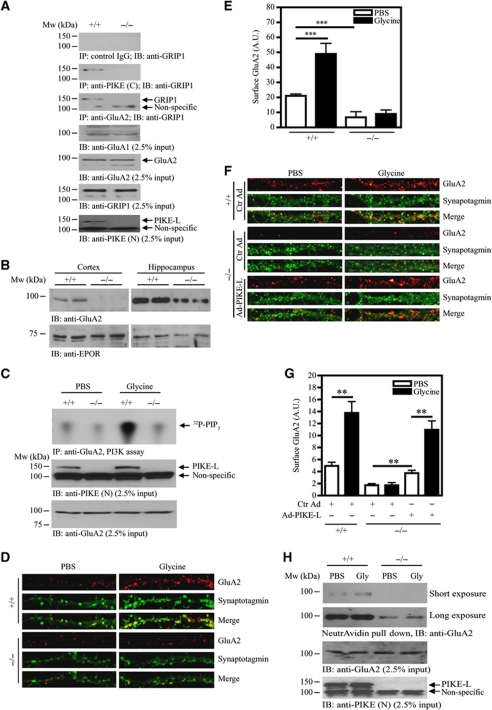
Figure 4.
Glycine-induced cell-surface expression of GluA2 is impaired in PIKE−/− neurons. (A) The association of GluA2 and GRIP1 is reduced in PIKE−/− brain. Immunoprecipitations from WT (+/+) and PIKE knockout (−/−) mouse brain lysates using control IgG (first panel), anti-PIKE-L C-terminal antibody (PIKE (C)) (second panel) and anti-GluA2 (third panel) were performed and the associated GRIP1 was detected using anti-GRIP1 antibody. The expression of GluA1 (fourth panel), GluA2 (fifth panel) and GRIP1 (sixth panel). The level of PIKE-L (seventh panel) was also examined using anti-PIKE-L N-terminus (PIKE (N)) antibody. (B) Surface expression of GluA2 is reduced in PIKE−/− brain. Plasma membrane were isolated from the cortex and hippocampus of age-matched (3-month-old) WT (+/+) and PIKE−/− (−/−) mice. The expression of GluA2 was determined by immunoblotting analysis (upper panel). Expression of EPO receptor was also determined as a loading control (lower panel). (C) Glycine-induced GluA2-associated PI3K activity is abolished in PIKE−/− neurons. After treated with glycine (200 μM), the GluA2 in WT (+/+) and PIKE-knockout (−/−) cortical neurons (10 DIV) was immunoprecipitated for PI3K assay (top panel). The expression of PIKE-L (middle panel) and GluA2 (bottom panel) in the cortical neurons were verified using anti-PIKE-L N-terminus (PIKE (N)) antibody and anti-GluA2, respectively. (D) Cell-surface expression of GluA2 under glycine treatment is impaired in PIKE−/− neurons. Hippocampal neurons (21 DIV) were stained with anti-GluA2 antibody under non-permeabilized condition and the cell surface GluA2 were visualized by confocal microscope. (E) Quantitation of cell surface GluA2 on neurons shown in (C) (***P<0.001, Student's t-test, n=8). Arbitrary units (A.U.) of GluA2 expression were shown. (F) Cell-surface expression of GluA2 is rescued in PIKE−/− neurons after PIKE-L overexpression. Hippocampal neurons (21 DIV) were infected with control adenovirus (Ctr Ad) or adenovirus overexpressing PIKE-L (AD-PIKE-L) for 48 h. The cells were then stimulated with PBS or glycine (200 μM, 20 min) and stained with anti-GluA2 antibody under non-permeabilized condition. (G) Quantitation of cell surface GluA2 on neurons shown in (F) (**P<0.01, Student's t-test, n=8). Arbitrary units (A.U.) of GluA2 expression were shown. (H) Biotinylation assay on cell-surface expression of GluA2. Cortical neurons (DIV 10) from WT (+/+) and PIKE knockout (−/−) mice were treated with glycine (200 μM). Cell-surface proteins were biotinylated, pulled down by NeutrAvidin beads and the amount of GluA2 was detected using immunoblotting analysis (top panel). The expressions of GluA2 (middle panel) and PIKE-L (bottom panel) were also examined using anti-PIKE-L N-terminus (PIKE (N)) antibody and anti-GluA2, respectively.