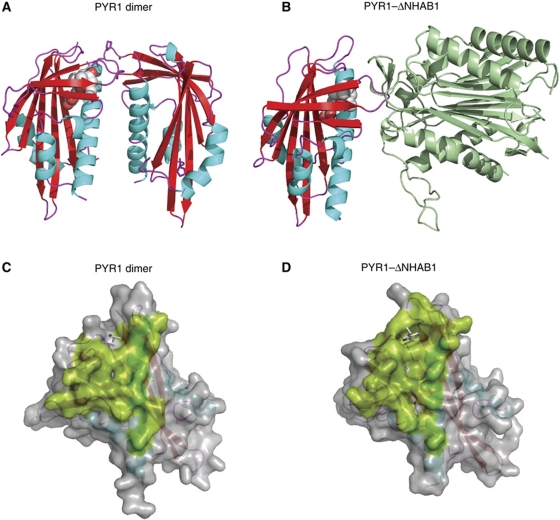
Figure 1.
The PYR/PYL/RCAR dimerization and phosphatase interaction regions. The structures of the PYR1 dimer (3K90) (A) and the PYR1–ABA–ΔNHAB1 ternary complex (3QN1) (B) are shown. The abscisic acid molecule is shown in CPK representation. The PYR1 molecular surfaces involved in dimerization (C) and ΔNHAB1 interaction (D) are shown in green colour. The side chains of the Leu 87, from the ABA-free subunit of the PYR1 dimer (C) and the side chain of Trp 385 from ΔNHAB1 (D) that occupy similar positions near the PYR1 gating loops are indicated as stick models. The large degree of overlap between the two surfaces indicates that the PP2C-interaction region is occluded in the PYR1 dimer and that receptor dissociation would be required for the formation of the ternary complex.