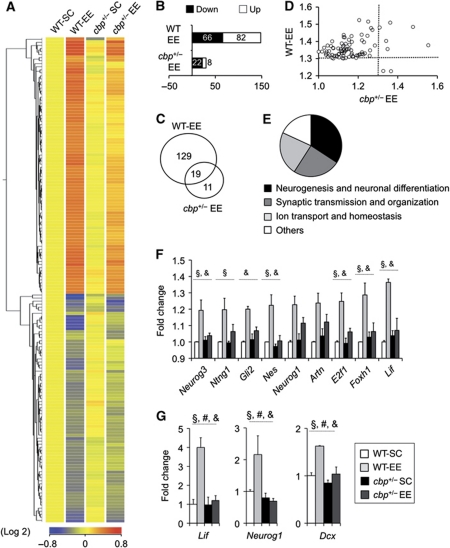
Figure 5.
Impaired neuroadaptative transcriptional response to EE in the hippocampus of cbp+/− mice. (A) The hierarchical cluster of the 159 TCs differentially regulated in response to EE (corrected P-value <0.05, FC>1.3) reveals an attenuated transcriptional response in cbp+/− mice. (B) Number of TCs upregulated (white) and downregulated (black) in response to EE in WT and cbp+/− mice (referred to the respective SC groups) with FC>1.3. (C) Venn diagram showing the number of EE-regulated TCs. (D) Scatter plot comparing, in WT and cbp+/− mice, the FC of the 84 TCs differentially upregulated in response to EE. The dotted line indicates the threshold for FC. Most dots are located in the upper left quadrant, indicating that the changes are larger in WT animals. r(82)=0.31, P<0.05. (E) Pie diagram showing the number of unique entities associated to a GO term in each of the major functional categories identified in the analysis of gene sets differentially expressed in EE mice. (F) Bar graph showing the expression level of specific neurogenesis-related genes whose induction by EE is impaired in cbp+/− mice (expression values extracted from microarray data). Two-way ANOVA, §: significant genotype effect, &: significant genotype × housing interaction (non-corrected P-values). All these genes show a significant housing effect. Some interesting genes showing borderline significance are also presented. (G) qRT–PCR validation of EE-mediated hippocampal induction for the neurogenesis-related genes lif, neurog1 and dcx. Two-way ANOVA, #: significant housing effect, §: significant genotype effect, &: significant genotype × housing interaction; n=3 per group.