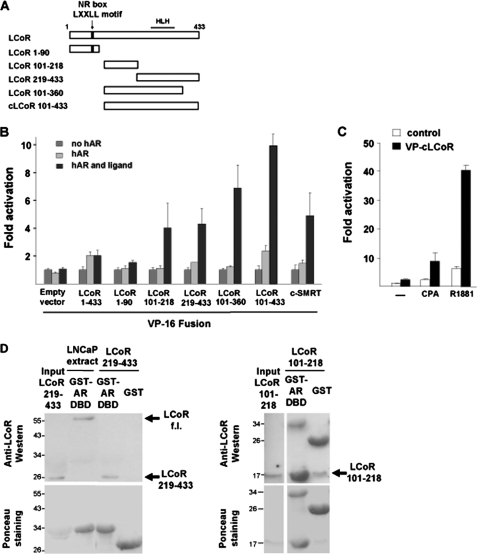
FIGURE 4.
LCoR deletion analysis: Requirement of two interaction domains. A, LCoR is a 433-amino acid protein with a single NR-box for interaction with selected members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily. The C-terminal part of LCoR harbors an HLH interaction motif. VP16-cLCoR was constructed by cloning the last 332 C terminus amino acids into the pCMX-VP16 empty vector. B, CV1 cells were transfected with MMTV-Luc, VP16, or various VP16-LCoR fusions (1 μg) and treated with CPA. Data were plotted setting each empty vector control VP16 in the absence of hormone arbitrarily as 1 and represent fold reporter activation. C, CV1 cells were transfected with pMMTV-Luc, pCMX-VP16-cLCoR (2 μg), and hAR (50 ng) treated with R1881 or CPA. The graph depicts the fold hormone induction. LCoR binding to AR was significant for B and C (Student's t test, p < 0.05). D, bacterially expressed GST or GST-AR-DBD were affinity-purified and incubated with either 0.5 mg LNCaP whole cell extract, as positive control for full-length LCoR (f.l.) binding to the AR-DBD, or with 10 μg of His-tagged bacterially expressed and purified LCoR 219–433 or 101–218 fragments that were detected by Western blotting. Ponceau staining served as a loading control. Both LCoR minimal domains show significant binding to the AR-DBD.