FIGURE 5.
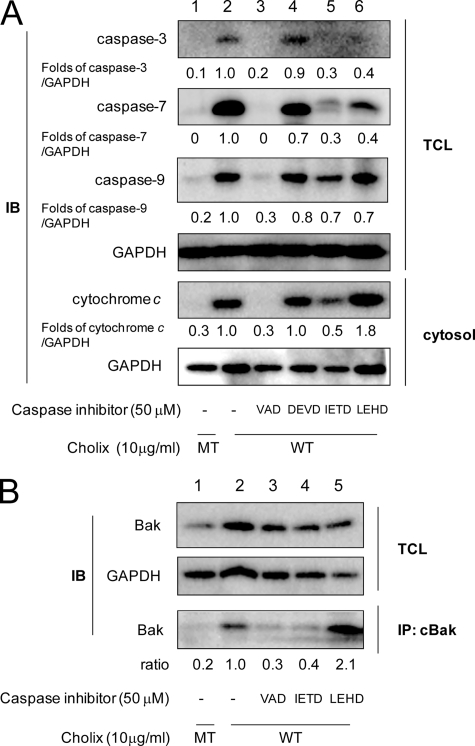
Effects of caspase inhibitors on Cholix-induced apoptotic signals. A, cells were grown overnight and then pretreated with the indicated caspase inhibitors (50 μm) as follows; VAD, general caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK; DEVD, caspase-3 inhibitor Z-DEVD-FMK; IETD, caspase-8 inhibitor Z-IETD-FMK; and LEHD, caspase-9 inhibitor Z-LEHD-FMK. After 40 min, cells were incubated for 18 h with wild-type (WT) or mutant (MT) Cholix (10 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of the inhibitor. Lysates were collected from cells and resolved by immunoblotting to detect the indicated caspase cleavages. Cells were incubated with WT or MT Cholix (10 μg/ml) for 18 h, and then the cytosolic fraction was collected as described previously (18). Cytochrome c release into cytosol was detected using an anti-cytochrome c antibody. Mean values were calculated on relative band intensity in three separate experiments. B, cells were pretreated with the indicated caspase inhibitors (50 μm) for 40 min, and then incubated for 9 h with WT or MT Cholix (10 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of the inhibitor. Cells were lysed and immunoprecipitation with anti-conformation-specific Bak (cBak) antibody as described in Fig. 4. The top and middle panels show the total cell lysate (TCL), and the bottom panel shows Bak, which was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-cBak antibody. Mean values were calculated on relative band intensity in three separate experiments.