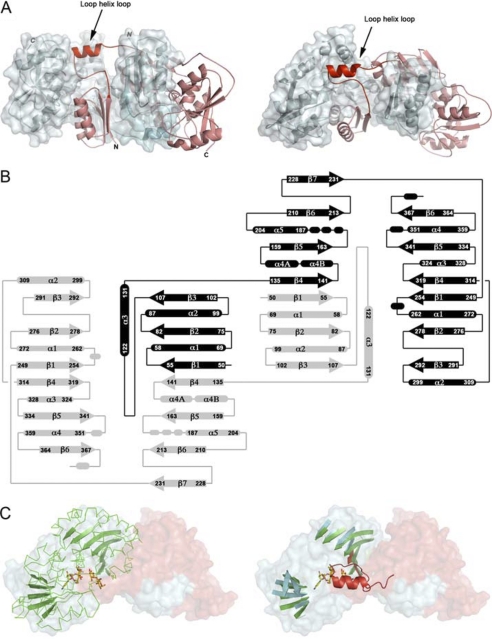
FIGURE 1.
A, shown is the NST domain-swapped homodimer. The two polypeptide chains are colored in red (α) and blue (β). In addition, the β subunit is displayed with an opaque solvent-accessible surface to show the extensive contact surface for the α subunit. The N-terminal 29 amino acid residues corresponding to a transmembrane helix were truncated from the N terminus (labeled). The loop-helix-loop highlights the swapping hinge module (Leu-108—Lys-134). B, the secondary structure topology diagram is shown. The two polypeptide chains are shaded in black and gray. The labeled numbers correspond to the amino acid residues in the NST protein sequence. The secondary structures are labeled as α for α helices and β for β strands and are numbered successively in the polypeptide chain. Residues 108–134 correspond to the hinge loop module in the NST swapped dimer. C, PmST1 (P. multocida) sialyltransferase is superimposed to one-half of the NST dimer. Left, the domain-swapped NST homodimer is shown in a solvent-accessible surface representation and is colored in red for the peptide chain α and blue for the peptide chain β. PmST1 is shown in green ribbon with the central β-sheets highlighted as arrows. The co-crystallized CMP-3F(axial)-Neu5Ac and lactose in PmST1 are shown in yellow-red stick representation. Right, the green ribbons of PmST1 are omitted for clarity. The figure shows the superimposition of the central β sheets between the PmST1 and one functional subunit in NST. The swapping hinge loop module (loop-helix-loop) colored in red is superimposed to the acceptor lactose in the PmST1 complex structure.