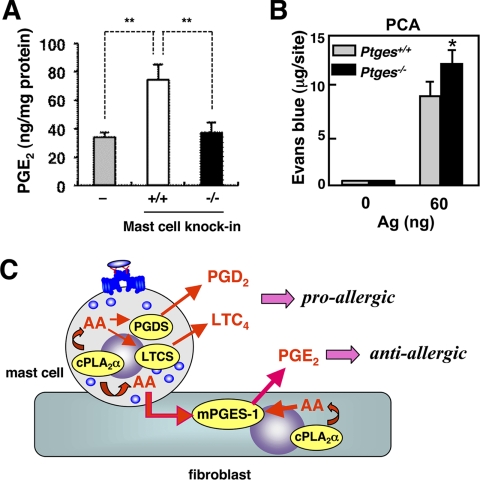
FIGURE 7.
Mast cell cPLA2α-dependent biosynthesis of anti-anaphylactic PGE2in vivo. A, Pla2g4a+/+ or Pla2g4a−/− BMMCs were subcutaneously transferred into the ears of mast cell-deficient KitW-sh/W-sh mice. After 2 days of reconstitution, PGE2 levels in the ears of KitW-sh/W-sh mice (−), those transferred with Pla2g4a+/+ BMMCs (+/+), and those transferred with Pla2g4a−/− BMMCs (−/−) were quantified (mean ± S.E., n = 12, **, p < 0.01). B, IgE-sensitized Ptges+/+ and Ptges−/− mice were challenged with or without Ag to assess PCA reaction (mean ± S.E., n = 3; *, p < 0.05 versus replicate Ptges+/+ mice). C, schematic diagram of the dual role of cPLA2α in mast cells for the production of pro-allergic and anti-allergic lipid mediators. In mast cells, cPLA2α supplies AA (via COX-1 and -2, which are omitted in the figure) to hematopoietic PGD2 synthase (PGDS) and LTC4 synthase (LTCS) for the biosynthesis of pro-allergic PGD2 and LTC4, respectively (64). In adjacent fibroblasts, AA is supplied by cPLA2α intrinsically expressed in fibroblasts (cell autonomous pathway) and by cPLA2α in mast cells (transcellular pathway) to mPGES-1 for the biosynthesis of anti-allergic PGE2.