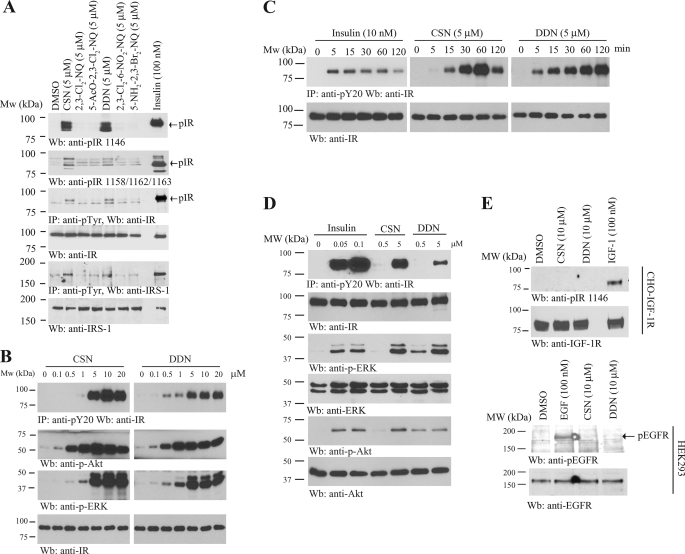
FIGURE 2.
DDN and CSN activate IR and its downstream signaling. A, DDN and CSN activate IR and its downstream signaling in CHO-IR cells. CHO-IR cells were treated with insulin (100 nm) or various 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives (5 μm) for 15 min. The cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-IR antibodies, or immunoprecipitated by pY20 and analyzed using anti-IR and anti-IRS-1, respectively. B, DDN and CSN induce IR phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. CHO-IR cells were treated with the small compounds at different concentrations for 15 min, and the IR phosphorylation was monitored by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. C, DDN and CSN induce IR phosphorylation in a time-dependent manner. CHO-IR cells were treated with DDN (5 μm), CSN (5 μm), and insulin (10 nm) for various times, and the IR phosphorylation was monitored by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. D, DDN and CSN induce IR phosphorylation and its downstream signaling in a dose-dependent manner. CHO-IR cells were treated with various concentrations of DDN or CSN for 30 min, or insulin for 15 min, and the IR phosphorylation and its downstream signaling were monitored by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. E, DDN and CSN cannot induce IGF-1R or EGFR phosphorylation. CHO-IGF-1R or HEK293 cells were treated with EGF (100 nm), IGF-1 (100 nm), DDN (10 μm), or CSN (10 μm) for 15 min. The cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-pIGF-1R and anti-pEGFR.