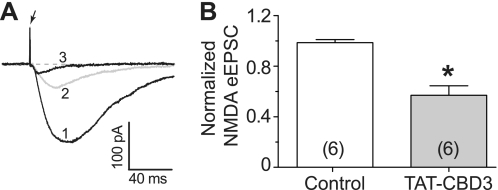
FIGURE 6.
Attenuation of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents by TAT-CBD3 in cortical neurons. A, representative recordings from a cortical neuron showing overlaid traces of a base-line control (1), TAT-CBD3 perfused (20 μm, 10 min) (2), and following the addition of NMDA antagonist (RS)-3-(2-Carboxypiperazin-4-yl)-propyl-1-phosphonic acid (RS)CPP)) (1 μm) (3). The arrow represents a stimulation artifact. Holding potential was −60 mV. B, pooled data displaying normalized NMDA-mediated current in control and after perfusion with TAT-CBD3 (20 μm) perfusion. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E. (error bars) (n = 6). The addition of TAT-CBD3 caused a significant reduction of NMDA-mediated eEPSC from cortical neurons (*, p < 0.01 versus control, Student's t test).