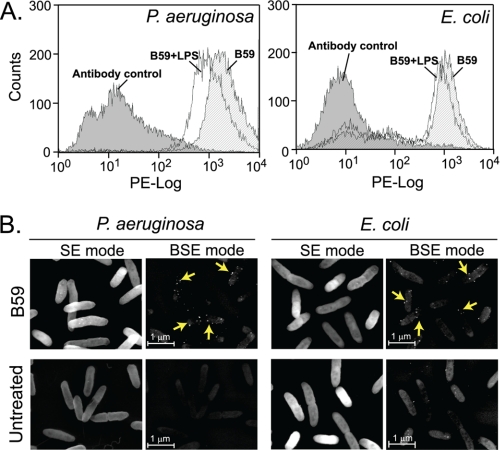
FIGURE 8.
LPS-binding peptide, B59, associates with Gram-negative bacteria. A, the binding of B59 to GNB was analyzed by flow cytometry. E. coli and P. aeruginosa were treated with 1 mm B59 for 30 min, with (white) or without (stripes) pre-treatment with 100 ng/ml LPS. The peptide bound to the bacterial surface was detected using primary rabbit anti-Hb antibody (1:400) and secondary phycoerythrin-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:200). The fluorescence intensity is plotted in log-fluorescence units versus counts. The negative control bacteria incubated without the peptide are indicated in gray. The results are representative of three independent experiments. B, the association of B59 to the bacterial surface was visualized using scanning electron microscopy coupled with immunogold labeling. Specific binding of the peptide is demonstrated by the colloidal gold (arrows) observed under backscattered electron (BSE) mode. Untreated bacteria served as negative control. Magnification is 15,000×. Bar, 1 μm.