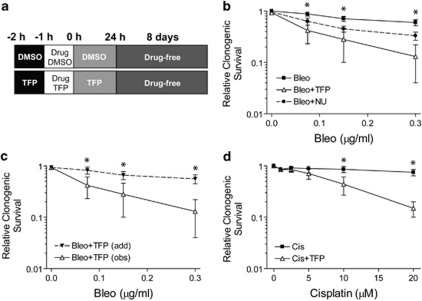
Figure 1.
TFP potentiates DNA damage-induced killing of human lung cancer cells. Clonogenic capacity was determined for U1810 cells exposed to DNA-damaging drugs alone or in combination with TFP or NU7026 (both 10 μM). (a) Outline of drug co-treatment schemes: pre-treatment with 24 h post-incubation. For the sake of simplicity, only TFP co-treatment was shown, although the same strategy was also employed for other chemosensitizers. (b) TFP co-treatment markedly reduced the clonogenic capacity of cells exposed to bleomycin. (c) Comparison between the theoretical dose-response curve assuming additivity between bleomycin and TFP (add), as calculated from the Bliss additivism model, with the observed experimental data (obs) indicated that the combinatorial effect was supra-additive. (d) TFP significantly reduced the clonogenic capacity of cells exposed to cisplatin. Mean and S.D. were compiled from at least three independent experiments performed in duplicates (*P<0.05, TFP co-treatment versus single-agent bleo/cis treatment)