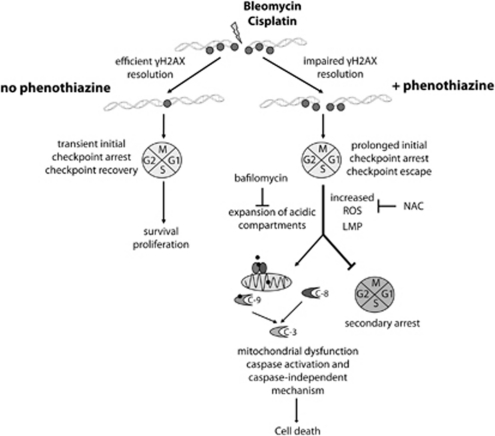
Figure 8.
A working model for phenothiazine-mediated chemosensitization. Phenothiazines impair the resolution of γH2AX in human lung cancer cells that were exposed to DNA-damaging chemotherapy, causing prolonged checkpoint arrest followed by checkpoint escape, defective mitosis, secondary arrest and/or cell death. TFP co-treatment enhances the intracellular production of ROS, LMP and the subsequent uncontrolled expansion of acidic (lysosomal) compartments. The mode of cell death exhibits many molecular features associated with apoptosis, including chromatin fragmentation. Both caspase-dependent and caspase-independent mechanisms contribute to phenothiazine-mediated chemosensitization. C, caspase