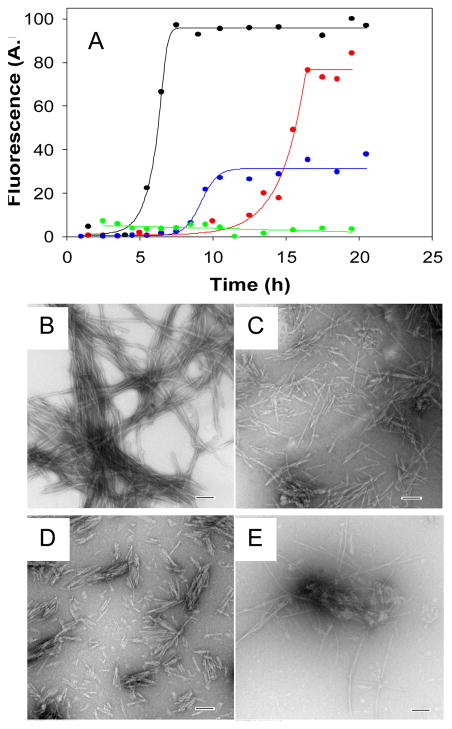
Figure 3.
Synergistic inhibition of amyloid formation by the Aβ1-40 polypeptide. (A) The results of fluorescent detected thioflavin-T binding assays are displayed. Black, Aβ1-40; Red, a1:1 mixture of Aβ1-40 with G24P-IAPP; Blue, a 1:1 mixture of Aβ1-40 with I26P-IAPP; Green, a 1:0.5:0.5 mixture of Aβ1-40 with G24P-IAPP and I26P-IAPP. (B) TEM image of Aβ1-40 alone. (C) TEM image of a1:1 mixture of Aβ1-40 and G24P-IAPP. (D) TEM image of a 1:1 mixture of Aβ1-40 and I26P-IAPP. (E) TEM image of a 1:0.5:0.5 mixture of Aβ1-40, G24P-IAPP and I26P-IAPP. Scale bars represent 100 nm. Aliquots were removed from the kinetic experiments 20 hours after amyloid formation was initiated and TEM images collected. The kinetic assays depicted in panel (A) were carried out in 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) with continuous stirring at 25°C. The total concentration of inhibitor was the same in the 1:1 mixtures and in the 1:0.5:0.5 mixtures and was equal to 24 μM. Aβ1-40 was at 24 μM.