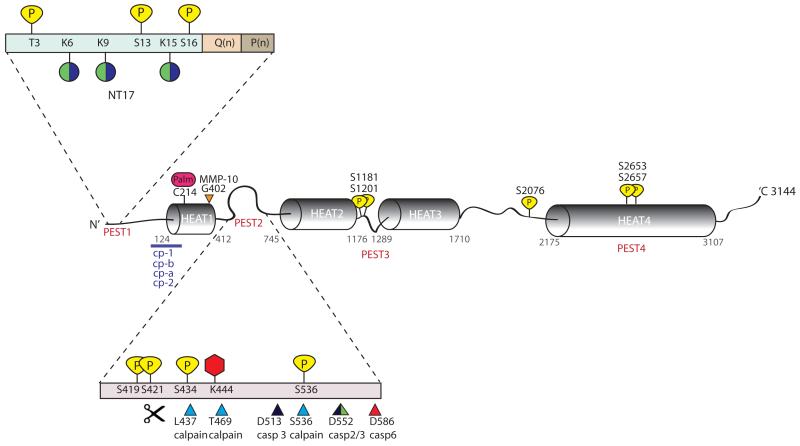
Figure 1. Schematic representation of htt protein and its PTMs.
Predicted HEAT repeats and PEST domains are marked along the length of the htt protein. PEST 1 domain (containing the first N-terminal 17 amino acids (NT17), polyglutamine tract Q(n) and polyproline sequence P(n)) and PEST 2 domain have been magnified to show the large number of clustered post-translational modifications in these regions. Phosphorylation sites at threonine (T) or serine (S) residues are indicated in yellow. Lysines (K) which are modified either by the addition of ubiquitin or sumo-1 are indicated by green and purple coloured circles. Acetylation at lysine (K) 444 is represented as a red hexagon and palmitoylation at cysteine (C) 214 is represented as a pink oval. Protease cleavage sites are marked by triangles; calpain sites are indicated in blue, caspase −2, −3 and −6 sites are indicated by green, black, and red, respectively and matrix metalloprotease-10 (MMP-10) site at 404 is indicated in orange. Additional proteolytic cleavage sites lie at the N-terminus of htt and predicted cleavage regions between residues 81-214 are indicated by a purple line. Cleavage between amino acid 104-114, 205-214, 81-129 and at R167 generate cp-A, cp-B , cp-1 and cp-2 fragments, respectively.