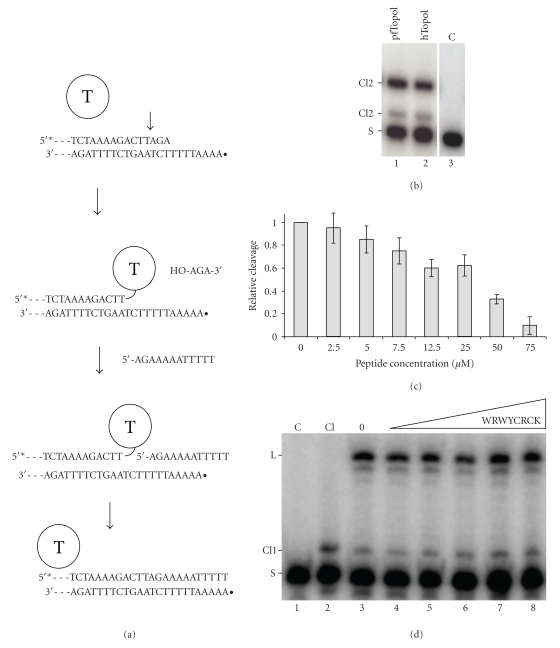
Figure 2.
Effect of peptide WRWYCRCK on pfTopoI-mediated DNA cleavage. (a) Schematic depiction of the cleavage and religation reactions. The substrate (OL19/OL27) used for assaying cleavage allows covalent attachment of the enzyme to the 3′ end of the 5′-radiolabeled scissile strand (OL19) by cleaving off a trinucleotide. Ligation is prevented by diffusion of the trinucleotide. To initiate ligation, the ligator strand (OL36) is added to covalent cleavage complexes generated by incubating pfTopoI with radiolabeled OL19/OL27. (b) Gel picture showing the cleavage products obtained by incubating 5′-radiolabeled OL19/OL27 with pfTopoI (lane 1) or hTopoI (lane 2). (c) Graphical depiction of the cleavage activity of pfTopI plotted as a function of peptide WRWYCRCK concentration. The cleavage activity was calculated as described in Section 2. (d) Representative gel picture showing the ligation activity of pfTopoI in the presence of peptide WRWYCRCK at the following concentrations: 1.3 μM, 2.5 μM, 5 μM, 7.5 μM, or 12.5 μM. T: topoisomerase I; asterisk: 5′-radiolabel with [γ-32P]; filled circle: 5′-cold phosphorylation; S: substrate; Cl1: cleavage product resulting from cleavage at the black arrow in the schematic depiction; Cl2: cleavage product resulting from cleavage two nucleotides upstream of the black arrow in the schematic depiction; C: negative control lanes without any enzyme added; Cl: cleavage control lane without ligator strand added; 0: positive control lane with pfTopoI but no peptide added.