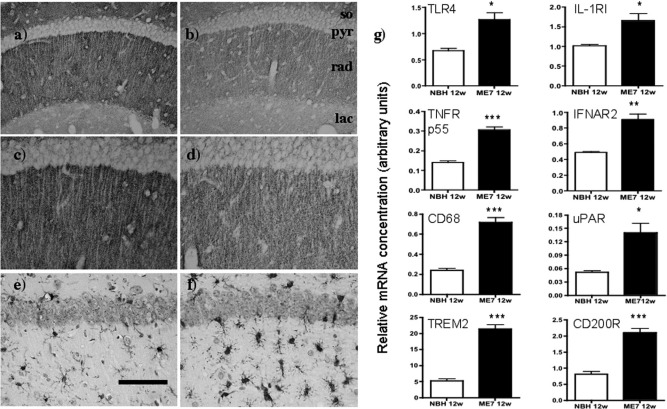
Fig. 1.
Hippocampal vulnerability: synaptic loss and inflammatory priming. Presynaptic terminals in the stratum oriens (so), stratum radiatum (rad) and stratum lacunosum moleculare (lac) of the hippocampus, visualized by immunostaining with sy38 anti-synaptophysin in NBH (a and c, ×20 and ×40, respectively) and ME7 animals at 12 weeks postinoculation (b and d, ×20 and ×40, respectively). Increased microglial numbers and activation state in the same region of NBH (e) and ME7 animals (f), labeled using anti-IBA-1 antibody against microglia and visualized at ×20. (g) Hippocampal expression of the inflammatory receptors TLR4, IL-1R1, TNFR p55, and IFNAR2, microglial CD68 and uPAR and the myeloid-restricted anti-inflammatory markers TREM2 and CD200R in ME7 and NBH animals at 12 weeks. Significant differences by Student t test are denoted by * (p < 0.05), ** (p = 0.0027), and *** (p < 0.001). n = 9, ME7; and n = 4, NBH. Scale bar = 100 μm in a and b and 50 μm in c-f.