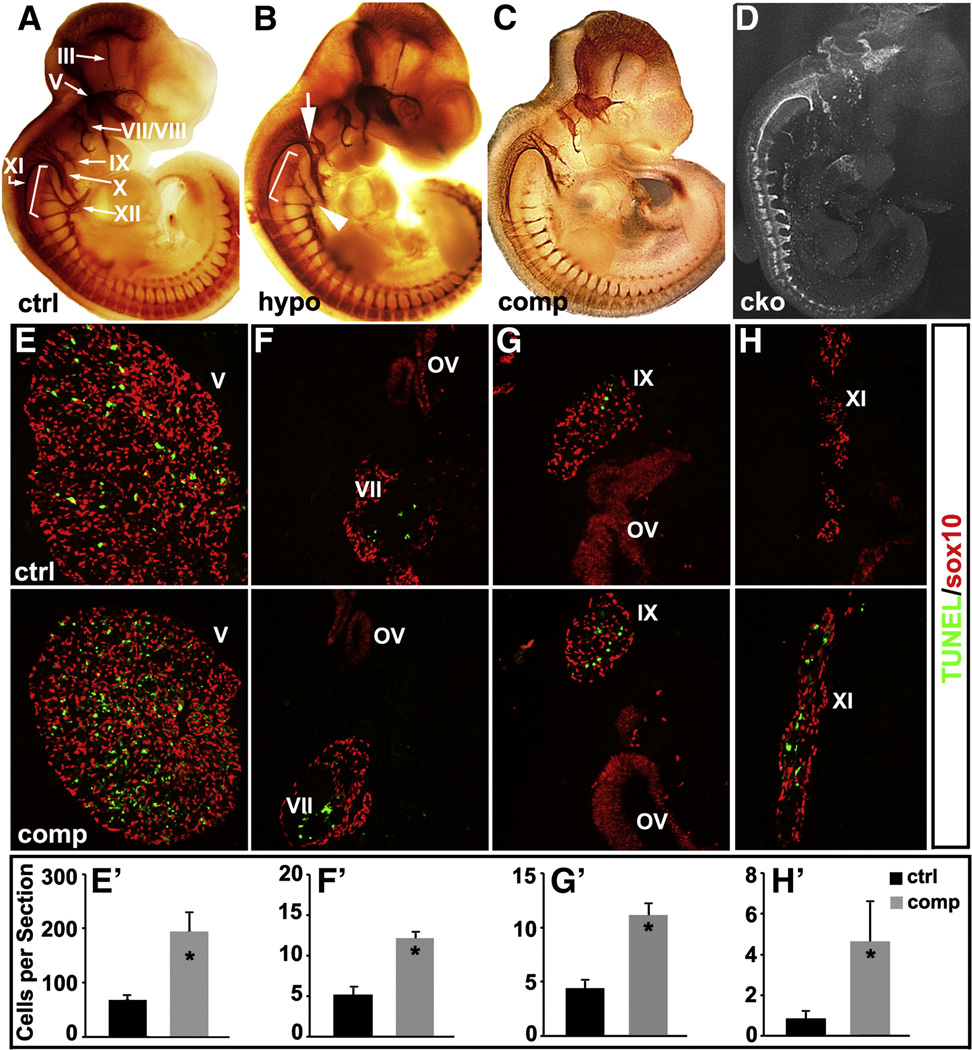
Fig. 2.
Reduced Isl1 expression in Isl1 compound mutant leads to increased apoptosis and abnormal development of cranial ganglia. Wholemount neurofilament staining of control (ctrl) (A), Isl1 hypomorphic (hypo) (B), Isl1 compound mutant (comp) (C) and Nestin-Cre; Isl1 conditional knockout (cko) (D) embryos at E11.5. Compared to control embryos, Isl1 hypomorphic mutant embryos displayed a relative normal size of cranial ganglia III, V, VII/VIII, X and XI (B). However, ectopic axonal projections from the cranial ganglion IX were observed (B, white arrow). Axonal projections of XI and XII ganglia were significantly reduced and blunted (B, bracket and arrowhead). In Isl1 compound mutant (C), further reduction in Isl1 expression led to reductions in the size of the cranial ganglia (V, VII/VIII, IX and X). Reductions in axon projections were observed in ganglia V (ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular branches), VII, IX, X, XI and XII (C). Nestin-Cre; Isl1 conditional knockout embryos displayed an overall developmental defect with severe reduction in the size of cranial ganglia and their axon projections (D). TUNEL staining at E11.5 revealed significantly increased apoptosis in the cranial ganglia V, VII, IX and XI of Isl1 compound mutant compared to control embryo (E–H and E′–H′).