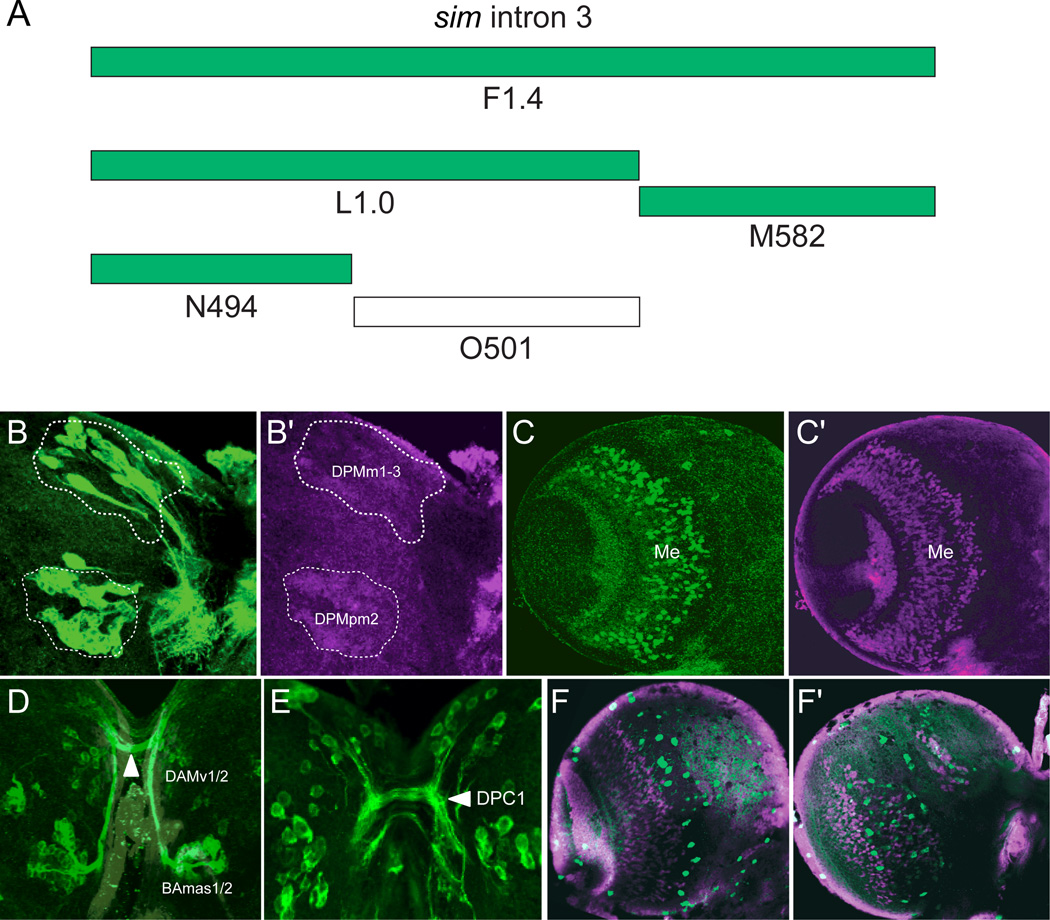
Fig. 5. Intron 3 subfragments drive expression in subsets of Sim+ cells.
(A) The schematic illustrates subfragments of the F1.4 fragment tested for postembryonic brain expression. Green blocks indicate Gal4 constructs that drive GFP in sim+ brain cells, and the unfilled block indicates an absence of Sim+ brain expression. (B,B’) L1.0-Gal4 drives UAS-mCD8-GFP expression in the DPMm1–3, DPMpm2, and PLSC neurons (not shown) on the posterior side of the brain. The brain was stained for GFP (green) and Sim (magenta), and the DPM clusters are circled. (C,C’) M582-Gal4 UAS-nuc-GFP expression drives GFP expression (green) in a subset of medullary neurons (Me). (D) N494-Gal4 UAS-tau-GFP reveals GFP expression (green) in the DAMv1/2 and BAmas1/2 Sim+ neurons on the anterior side of the brain. The BAmas1/2 axons project ipsilaterally before crossing the midline in the commissural tract (arrowhead) along with axons from DAMv1/2. (E) GFP+ cells with N494-Gal4 UAS-tau-GFP expression in the posterior brain overlap with DPM and PLSC neurons. Characteristic of the DPM neurons, the GFP-labeled neurons send their axons across the DPC1 commissure (arrowhead). (F,G) O501-Gal4 UAS-mCD8-GFP shows sporadic GFP+ cells on both the (F) anterior and (G) posterior sides of the brain that only coincidentally overlap with Sim+ neurons.