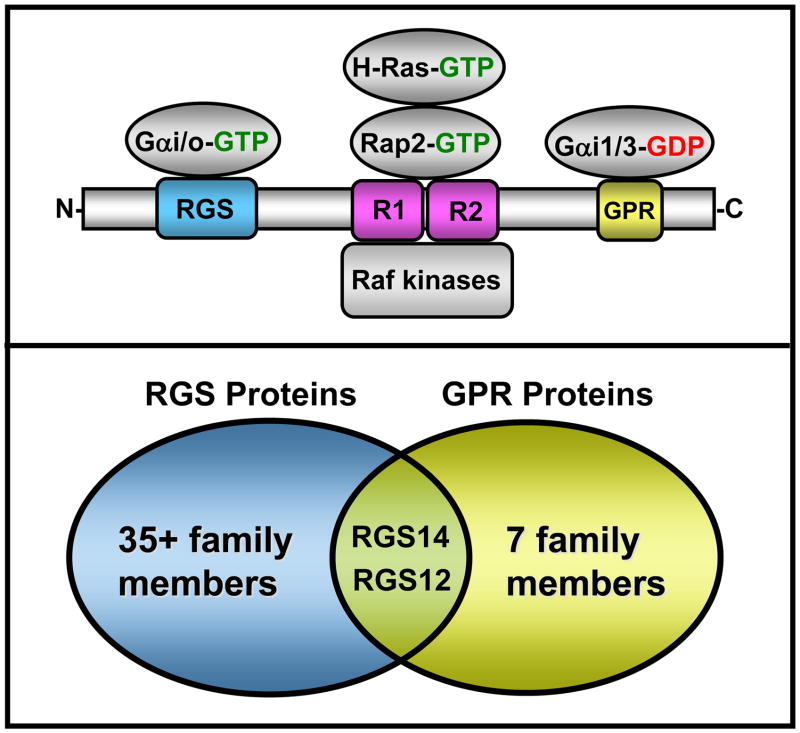
Figure 1. RGS14 domain structure and its identified binding partners.
Top: RGS14 directly binds activated Gαi family members and Gαo through its RGS domain, and it also specifically binds inactive Gαi1 and Gαi3 via its GPR domain. Activated H-Ras, Rap2, and Raf kinases directly interact with the Ras/Rap-binding domains (R1 and R2). Bottom: RGS14 is structurally and functionally unique in that it shares both an RGS domain and a GPR domain that places it and its closest relative RGS12 into both the RGS protein and the Group II AGS protein (GPR domain-containing) subfamilies.