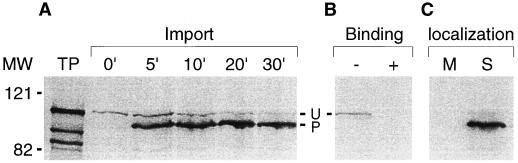
Figure 4.
ERD1 import, binding, and fractionation using pea chloroplasts. A, Import of ERD1 into pea chloroplasts was performed as described in Methods. Aliquots were removed at given times, and import was terminated by reisolating intact chloroplasts by sedimentation through a 40% Percoll cushion. Fractions were resuspended in sample buffer and subsequently analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. B, Binding of ERD1 to pea chloroplasts under low-ATP conditions. The binding reaction was equally divided into two fractions. One sample was treated with thermolysin (+) and the other sample was not (−). Protease digestion was allowed to continue for an additional 30 min on ice in the dark. Proteolysis was terminated by adding EDTA to a final concentration of 5 mm, and intact chloroplasts were reisolated by sedimentation through a 40% Percoll cushion with 5 mm EDTA present. C, ERD1 was imported into pea chloroplasts and fractionated as described in Methods. All fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. TP, Ten percent of translation product added to the import reaction; M, crude membrane pellet; S, supernatant fraction; U, unprocessed form of ERD1; P, processed form of ERD1; MW, Mr standards.