Fig. 2.
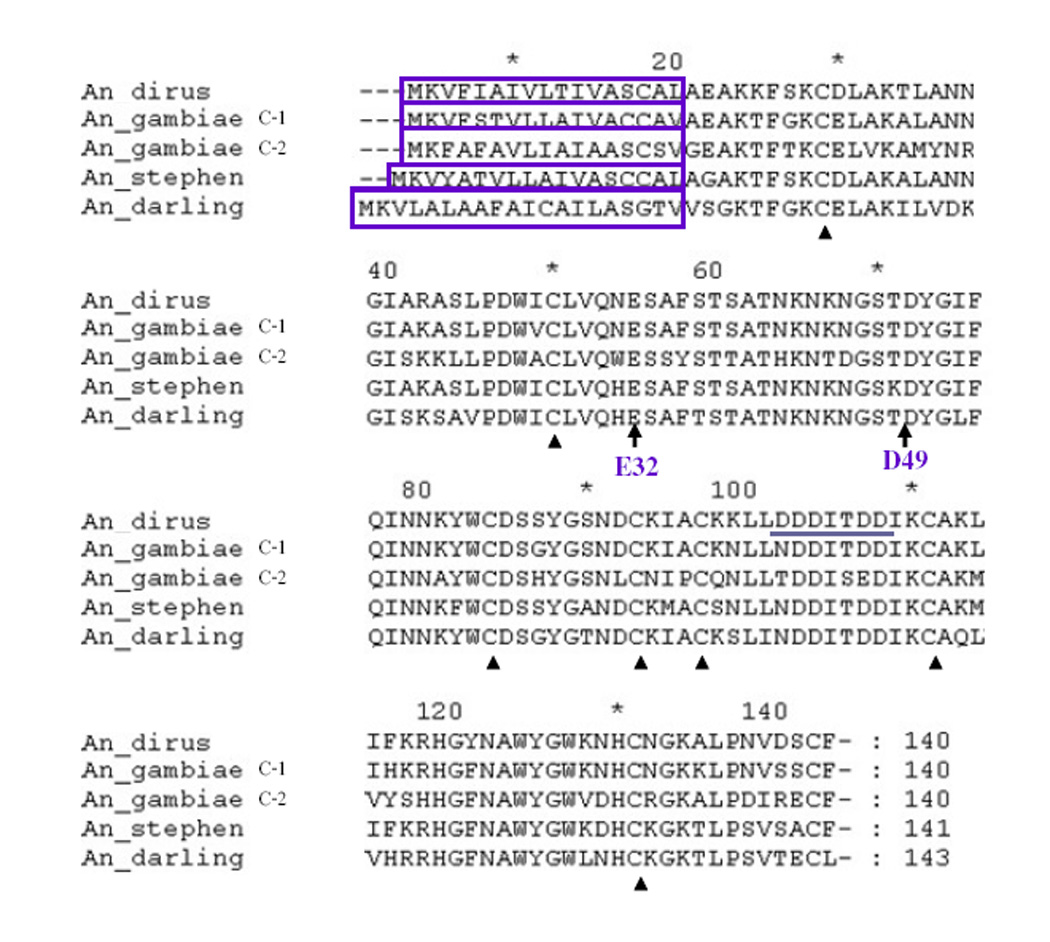
Alignment of deduced amino acid sequences of AdLys c-1 from An. dirus and other Anopheles mosquitoes. The predicted signal peptides are boxed. Conserved cysteines are marked with black triangles. E32 and D49, the two amino acids that are essential for muramidase function are denoted by black arrows. The potential calcium binding site (DDDITDD) from An. dirus Lys c-is underlined.
