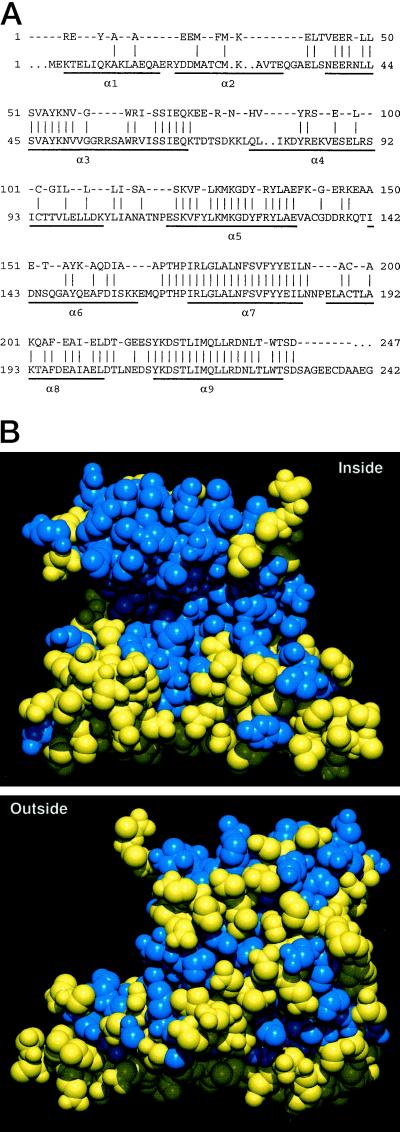
Figure 3.
Similarity between tomato 14-3-3 and human 14-3-3τ. A, Conserved regions in 14-3-3 proteins correspond to α-helices, as shown by amino acid sequence alignment between a consensus sequence derived from the six full-length tomato cDNAs and human 14-3-3τ. Only amino acids conserved between all six tomato sequences are shown (top line); identity between tomato and 14-3-3τ residues is indicated by a bar. Gaps (periods) were introduced to optimize the alignment. The regions that form the nine α-helices in the 14-3-3τ crystal structure are indicated by a line below the sequence. B, Sequence homology is mainly within the inner face of 14-3-3 proteins, as shown by a space-filling model of the 14-3-3τ protein crystal structure colored by homology with the tomato consensus shown in A. Identical amino acids are shown in blue, and nonidentical residues are shown in yellow. The upper inner face of the molecule, which corresponds to the C-terminal domain, shows high sequence conservation; whereas the lower inner face, corresponding to the N-terminal dimerization domain, and the whole outer face are poorly conserved.