Abstract
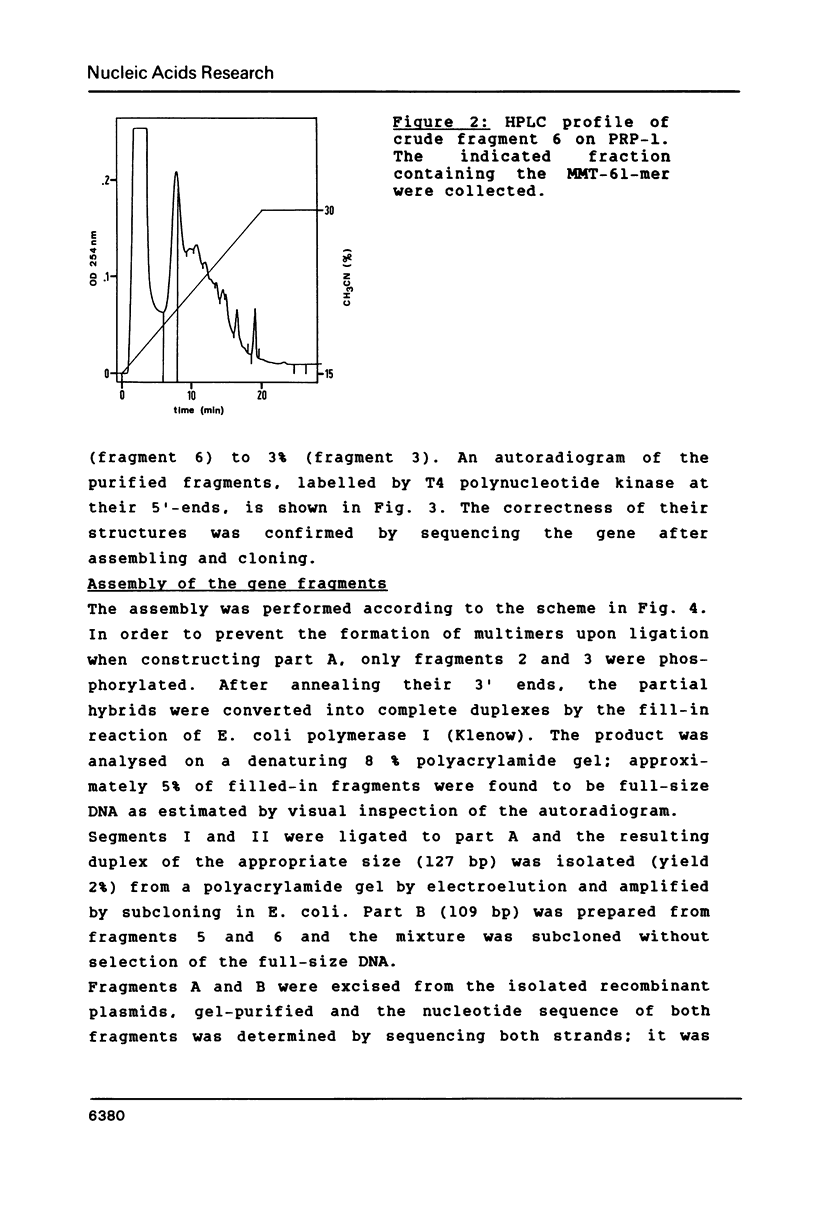
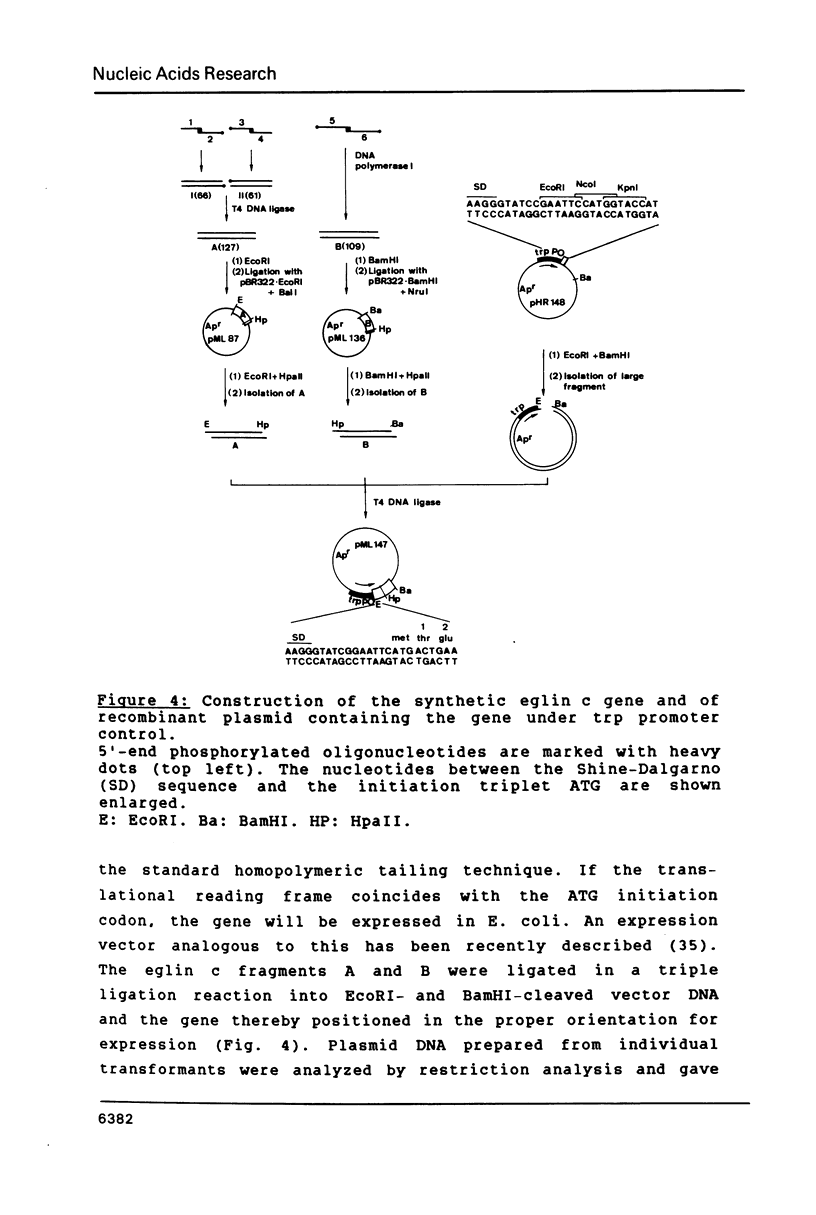
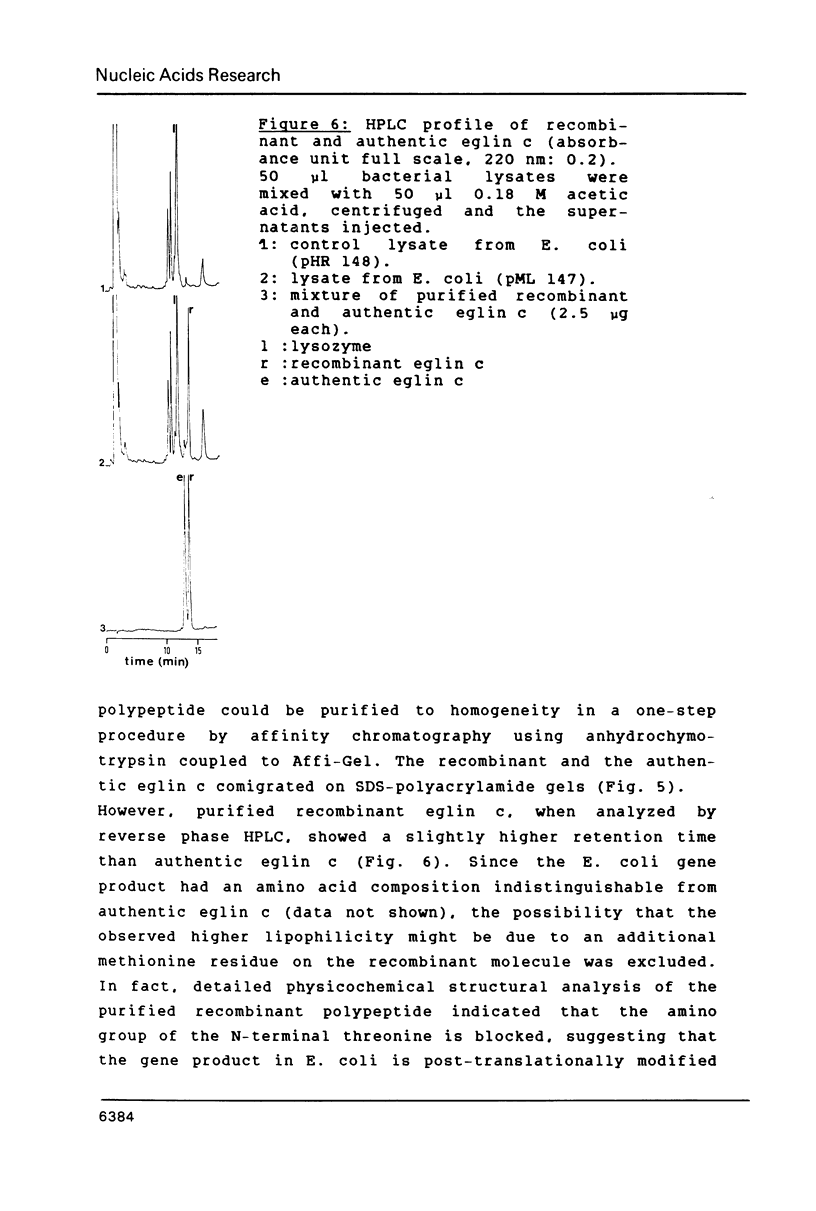
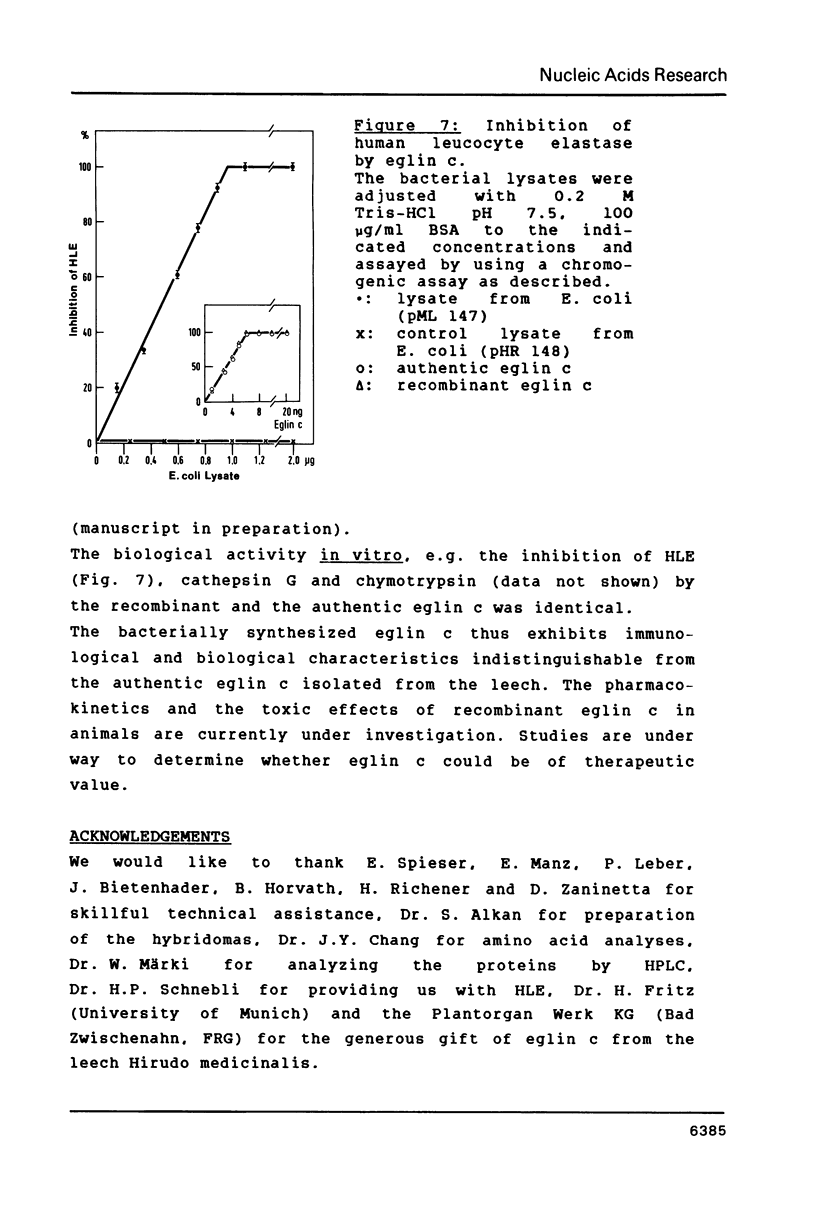
A DNA containing the coding sequence for the proteinase inhibitor protein, eglin c, from the leech Hirudo medicinalis has been obtained by enzymatic assembly of chemically synthesized DNA fragments. The synthetic gene consists of a 232 base-pair fragment containing initiation and termination codon signals with restriction enzyme recognition sites conveniently placed for cloning into a plasmid vector. Only six oligonucleotides from 34 to 61 bases in length, sharing pairwise stretches of complementary regions at their 3'-termini, were prepared by phosphotriester solid-phase synthesis. The oligomers were annealed pairwise and converted into double stranded DNA fragments by DNA polymerase I mediated repair synthesis. The fragments were assembled by ligation, and the synthetic gene was expressed in high yield in E. coli under the transcriptional control of the E. coli tryptophan promoter. The expression product was purified to homogeneity and was shown to have similar physicochemical and identical biological properties as the authentic protein isolated from the leech.
Full text
PDF














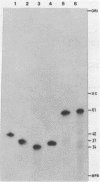
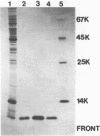
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ako H., Ryan C. A., Foster R. J. The purification by affinity chromatography of a proteinase inhibitor binding species of anhydro-chymotrypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1639–1645. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchi H., Khorana H. G. CV. Total synthesis of the structural gene for an alanine transfer ribonucleic acid from yeast. Chemical synthesis of an icosadeoxyribonucleotide corresponding to the nucleotide sequence 31 to 50. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 28;72(2):251–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge M. D., Green A. R., Heathcliffe G. R., Meacock P. A., Schuch W., Scanlon D. B., Atkinson T. C., Newton C. R., Markham A. F. Total synthesis of a human leukocyte interferon gene. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):756–762. doi: 10.1038/292756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge M. D., Greene A. R., Heathcliffe G. R., Moore V. E., Faulkner N. J., Camble R., Petter N. N., Trueman P., Schuch W., Hennam J. Chemical synthesis of a human interferon-alpha 2 gene and its expression in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6419–6435. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Garoff H., Lehrach H. A subcloning strategy for DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5541–5549. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Shepard H. M., Yelverton E., Leung D., Crea R., Sloma A., Pestka S. Synthesis of human fibroblast interferon by E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4057–4074. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Ike Y., Ikuta S., Itakura K. Solid phase synthesis of polynucleotides. VI. Further studies on polystyrene copolymers for the solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1755–1769. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht R., Seemüller U., Liersch M., Fritz H., Braun D. G., Chang J. Y. Sequence determination of eglin C using combined microtechniques of amino acid analysis, peptide isolation, and automatic Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 1;130(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90650-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G. F., Yanofsky C. Translation of the leader region of the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1457–1466. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1457-1466.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi K., Arentzen R., Huang T., Itakura K. Solid-phase synthesis of polynucleotides. IV. Usage of polystyrene resins for the synthesis of polydeoxyribonucleotides by the phosphostriester method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5507–5517. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Sato M., Saito A., Itoh S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Construction and application of a novel plasmid "ATG vector" for direct expression of foreign genes in Escherichia coli. DNA. 1983;2(4):265–273. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese C. B., Zard L. Some observations relating to the oximate ion promoted unblocking of oligonucleotide aryl esters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4611–4626. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. J., Kierzek R., Huang T., Walker P. A., Itakura K. An alternate method for synthesis of double-stranded DNA segments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9226–9229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemüller U., Eulitz M., Fritz H., Strobl A. Structure of the elastase-cathepsin G inhibitor of the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Dec;361(12):1841–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemüller U., Meier M., Ohlsson K., Müller H. P., Fritz H. Isolation and characterisation of a low molecular weight inhibitor (of chymotrypsin and human granulocytic elastase and cathepsin G) from leeches. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Sep;358(9):1105–1107. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.2.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., Cook E., Fotheringham I., Pheby S., Derbyshire R., Eaton M. A., Doel M., Lilley D. M., Pardon J. F., Patel T. Chemical synthesis and cloning of a gene for human beta-urogastrone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4467–4482. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]