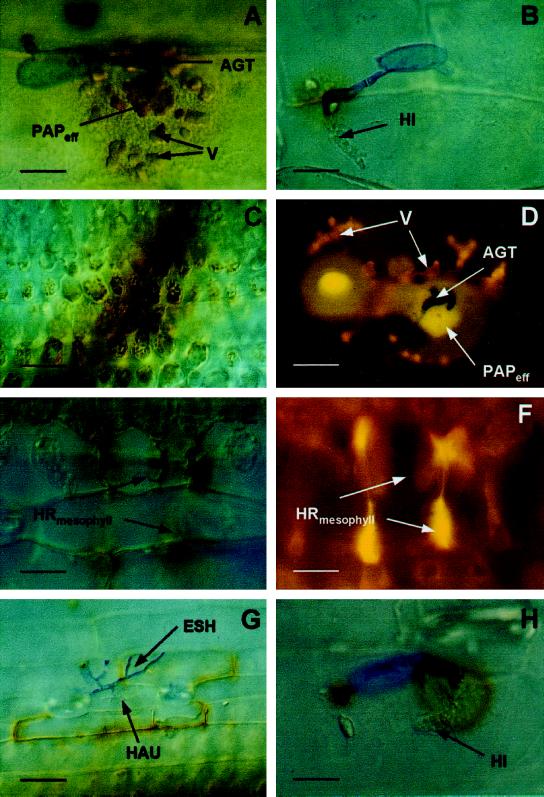
Figure 2.
Microscopic, subcellular localization of H2O2 at interaction sites in barley after inoculation with BghA6. Seven-day-old barley primary leaves of NILs were inoculated with 20 conidia mm−2 of BghA6. At different time points after inoculation, leaves were cut off, placed in a solution of 1 mg mL−1 DAB, and collected for microscopic analysis 8 h later (at the indicated time points). A, Effective papilla (PAPeff) in formation on cv Pallas (22 hai). Papilla and vesicles (V) with DAB polymers are seen beneath the appressorial germ tube (AGT). Scale bar = 8 μm. B, Successful penetration of cv Pallas (24 hai). The fungus had formed a haustorial initial (HI). Whereas the body of the ineffective papilla shows only a faint staining, the anticlinal cell wall close to the penetration site shows typical brownish DAB polymers. Scale bar = 10 μm. C, DAB staining of chloroplasts in healthy mesophyll cells neighboring a transverse vessel in cv Pallas primary leaves. Scale bar = 40 μm. D, BCPmlo5 (30 hai). Autofluorescence under UV-light excitation of effective papilla (PAPeff) halos and vesicles beneath primary and AGTs is indicative of the accumulation of phenolic compounds at a repulsed penetration attempt. Scale bar = 10 μm. E, BCPMla12 (48 hai): mesophyll HR subjacent to a living penetrated epidermal cell (out of focus). Dead cells show DAB staining. Scale bar = 20 μm. F, Epifluorescence microscopy of the interaction site shown in E. The cells in the center have collapsed. Accumulation of polyphenols is indicated by the yellow autofluorescence. Scale bar = 20 μm. G, BCPMla12 (48 hai): epidermal cells surrounding the penetrated, living cell show positive DAB staining, (Legend continues on facing page.)