Figure 1.
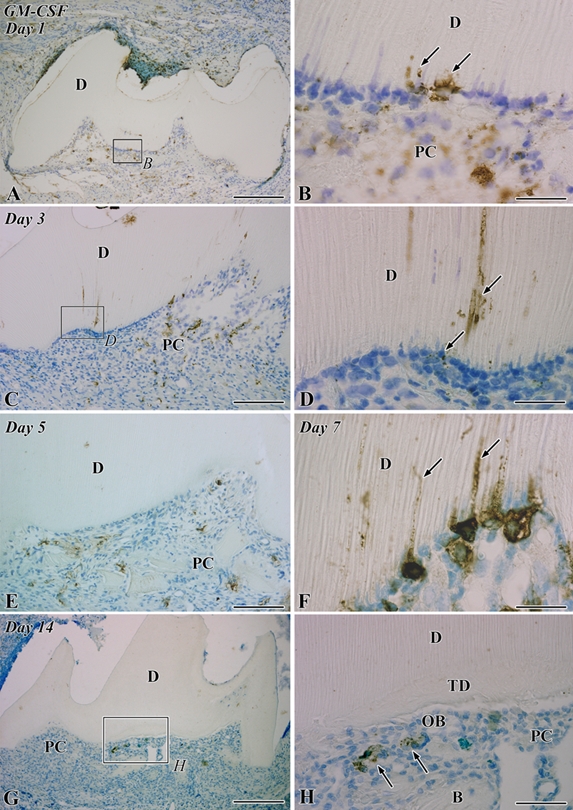
Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) immunoreactivity in the transplanted teeth at 1 (A, B), 3 (C, D), 5 (E), 7 (F), and 14 (G, H) days after operation. B, bone; D, dentin; PC, pulp chamber; TD, tertiary dentin. (A) GM-CSF-positive cells are distributed through the pulp chamber. (B) Higher magnification of the boxed area labeled by B in A. Some cells that extend their cellular processes into the dentinal tubules show GM-CSF-positive reactions (arrows). (C) The distribution pattern of GM-CSF-positive cells is the same as that in the previous stage. (D) Higher magnification of the boxed area labeled by D in C. GM-CSF-positive reactions are observed deeply in the dentinal tubules and in the cells arranging along the pulp-dentin border (arrows). (E) GM-CSF-positive reactions disappear from the pulp-dentin border and dentinal tubules, although GM-CSF-positive cells remain through the pulp chamber. (F) In the prolonged inflammatory lesions, GM-CSF-positive cells accumulate along the pulp-dentin border and extend their cellular processes into the dentinal tubules (arrows). (G) The distribution of GM-CSF-positive cells becomes sparse in the pulp chamber. (H) Higher magnification of the boxed area labeled by H in G. GM-CSF-positive cells (arrows) are located beneath the differentiated odontoblast-like cells (OB). Bars: A, G = 250 µm; C, E = 100 µm; H = 50 µm; B, D, F = 25 µm.
