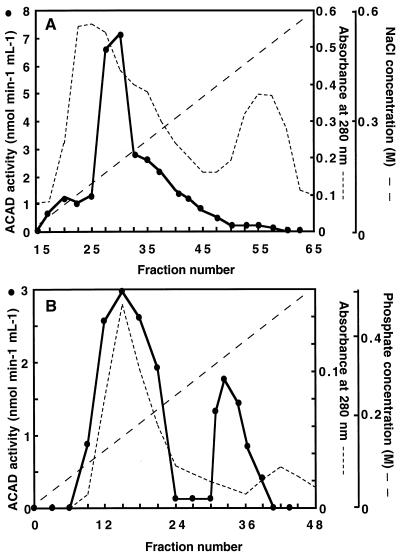
Figure 2.
Separation of distinct ACAD by column chromatography on DEAE-Sepharose (A) and hydroxylapatite-HT (B). Proteins from embryonic axes of early-germinating sunflower seeds were fractionated by ammonium sulfate precipitation as described in Methods. Column chromatography and ACAD activity measurements with 50 μm palmitoyl-CoA as the substrate were carried out as described in Methods. A, The resuspended 40% to 60% ammonium sulfate fraction was dialyzed and then loaded onto a DEAE-Sepharose column. Bound proteins were eluted by a linear NaCl gradient from 0 to 0.6 m. B, The pooled fractions from nos. 25 to 48 were concentrated and dialyzed before application to a hydroxylapatite-HT column. Bound proteins were eluted by a linear gradient of phosphate from 0 to 0.5 m. The two peaks of active fractions were pooled separately to give ACAD1 and ACAD2 preparations.