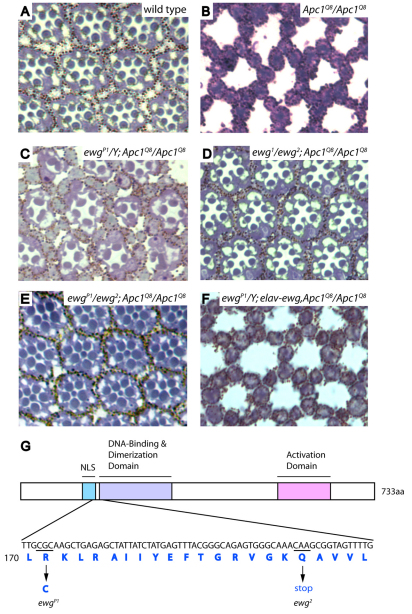
Fig. 1.
Ewg is required for photoreceptor apoptosis in response to Apc1 loss. (A-F) Cross-sections through adult retinas. (A) Eight photoreceptors are present in each ommatidium with seven photoreceptors visible in this section, arrayed in a trapezoidal pattern. (B) Upon Apc1 loss, all photoreceptors undergo apoptosis. The pigment cell lattice remains intact. (C-E) Photoreceptor apoptosis is prevented in hemizygous ewgP1 (C), transheterozygous ewg1/ewg2 (D) and ewgP1/ewg2 mutants (E). (F) Exogenous ewg expression driven by the elav promoter restores apoptosis in ewgP1; Apc1Q8 double mutants. (G) Schematic representation of the Ewg protein. A C-to-T substitution is found in ewgP1, resulting in an arginine to cysteine substitution in amino acid 171. In ewg2, an early stop codon at amino acid 178 is caused by substitution of C to T; no mutation was detected in the ewg-coding region in the ewg1 allele (G. Gill, personal communication).