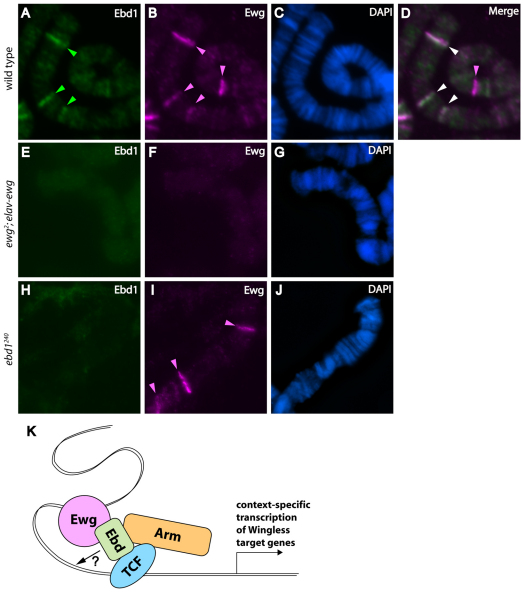
Fig. 7.
Ewg is required to recruit Ebd1 to chromatin. (A-J) Squashes of polytene chromosomes from third instar larvae, immunostained with Ebd1 (A,E,H) and Ewg antiserum (B,F,I). DNA is highlighted by DAPI staining (C,G,J). (A-D) Ewg and Ebd1 overlap at the majority of their binding sites in wild-type polytenes. (E-G) Ebd1 is not detectable on chromatin in the absence of Ewg. (H-J) Ewg association with chromatin is maintained in absence of Ebd1. (K) A model depicting function of Ewg and Ebd1 in context-specific Wingless signaling. Ewg associates with specific chromatin sites and recruits Ebd1. Ebd1 bridges Arm and TCF, stabilizing this complex, facilitating its recruitment to chromatin, and thereby promoting context-specific activation of a subset of Wingless target genes.