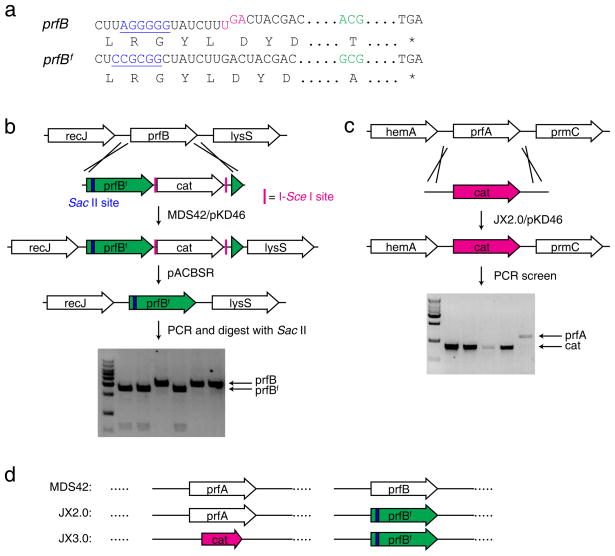
Figure 1. RF1 can be knocked out from E. coli after RF2 is fixed.
(a) Features of the RF2-encoding prfB gene in K-12 E. coli strains: an in-frame UGA stop codon (magenta) for autoregulation of RF2 expression and the Ala246Thr mutation (green) impairing RF2’s release activity for the UAA codon. In prfBf, the UGA regulation was removed and residue 246 reverted to Ala. A Shine-Dalgarno like sequence (blue) in prfB was silently mutated to a Sac II site (blue) in prfBf to facilitate the screening of prfBf knock-in. (b) Generation of the JX2.0 strain. The prfB gene in MDS42 was first replaced with prfBf followed by a Cm resistant cat cassette. The cat cassette was subsequently removed by pACBSR (see Supplementary Methods). (c) Generation of the JX3.0 strain. The RF1-encoding prfA gene was successfully knocked out with a cat cassette in JX2.0 to afford JX3.0. (d) Illustration of main features of the three strains, MDS42, JX2.0 and JX3.0.