Figure 3.
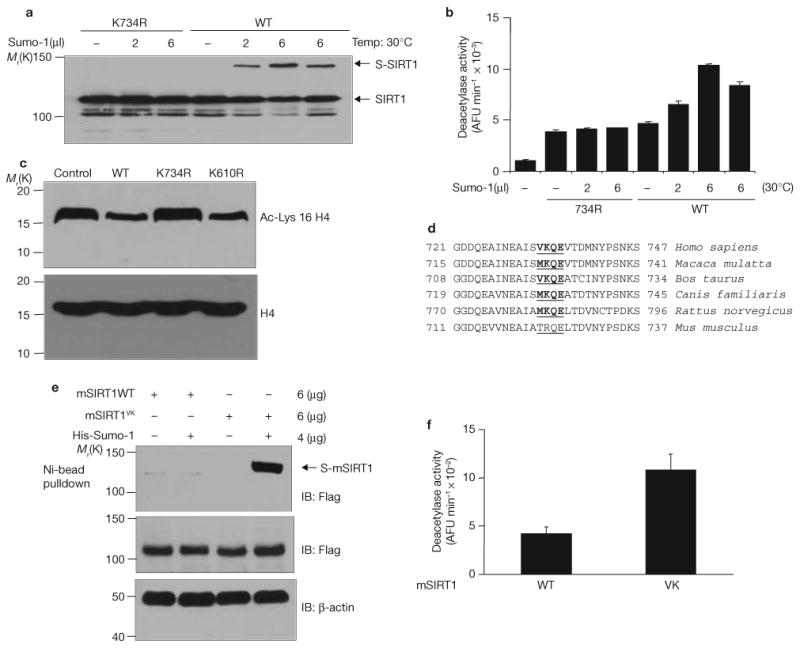
Sumoylation of SIRT1 at Lys 734 increases its intrinsic deacetylase activity. (a) Wild-type SIRT1 and K734R mutant were produced and purified in a cell-free system as His-tagged protein. In vitro sumoylation of SIRT1 was performed in the presence of indicated amounts of Sumo-1 and detected by immunoblotting of half of the reaction mixture with antibodies against SIRT1. (b) The other half of the reaction mixture described in a was assayed for deacetylase activity using a fluorometric assay system. Each data point is the average of triplicate (n = 3) samples analysed in parallel. The error bars represent s.d. AFU, arbitrary fluorescence unit. (c) Cells were transfected with wild-type Flag–SIRT1, Flag–SIRT1K734R or Flag–SIRT1K610R. Cell extracts were immunoblotted with antibodies against acetyl-Lys 16 of histone H4 or against histone H4. (d) Sequence alignment of the C-terminus of mammalian SIRT1 proteins. The four amino acids in comparison are underlined. The sumoylation consensus sites are shown in bold. (e) Cells were transfected with His–Sumo-1 together with Flag-tagged wild-type or mutant (VK) mouse SIRT1 (mSIRT1) in which Thr 722 and Arg6 723 were mutated to valine and lysine, respectively. His–Sumo-1 conjugated SIRT1 was isolated by nickel beads and detected by immunoblotting with antibodies against Flag. (f) Cells were transfected with Flag-tagged wild-type or mutant mouse SIRT1. Flag–SIRT1 was purified from cell extracts on M2-conjugated affinity columns and its deacetylase activity determined in vitro using a fluorometric assay system. Each data point is the average of triplicate samples (n = 3) analysed in parallel. The error bars represent s.d. Uncropped images of the scans are shown in the Supplementary Information, Fig. S1.
