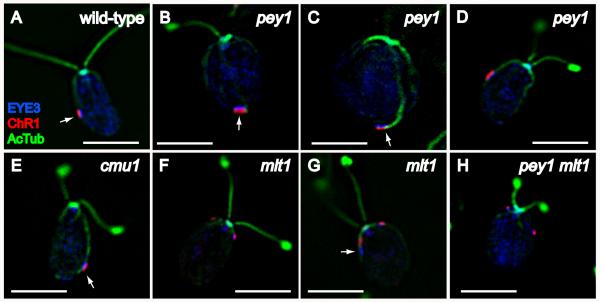
Figure 5.
Characterization of eyespot morphology and rootlet associations in wild-type C. reinhardtii and eyespot-positioning mutants. Combined immunofluorescence micrographs of methanol-fixed cells stained with anti-EYE3 (blue), anti-channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) (red), and anti-acetylated tubulin (green). A: Wild-type cell with equatorially-positioned eyespot, visible by the co-positioned layers of photoreceptor (red) and eyespot pigment granules (EYE3, blue). Note association of eyespot with the D4 rootlet (AcTub, blue). B-D: pey1 mutant cells exhibit a range of eyespot positions including posterior (arrows in B and C) and equatorial (D). Arrow in C highlights rootlet association. Eyespot morphology appears normal in pey1 cells. E: cmu1 mutant cell. The posteriorly-positioned eyespot is associated with the rootlet (arrow). F and G: Eyespots in mlt1 mutant cells are often anteriorly-positioned (F) and exhibit loss of co-positioning of photoreceptor with pigment granules (arrow in G). H: The pey1 mlt1 double mutant exhibits the multiple-eyespot phenotype of mlt1 including anterior eyespots. Bars, 5 μm.