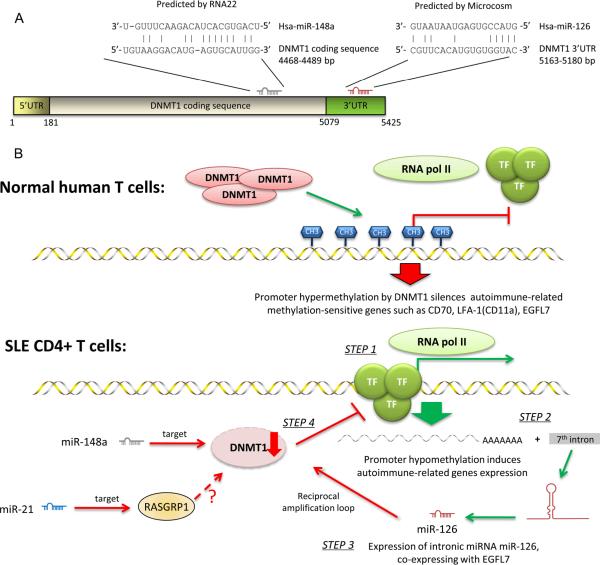
FIGURE 1.
MiR-21, miR-126, and miR-148a directly or indirectly regulate DNMT1 in SLE CD4+ T cells.
A. MiR-148a and miR-126 directly regulate DNMT1 validated experimentally. In particular, miR-148a binds to the DNMT1 coding sequence, as predicted by the program RNA22, while miR-126 binds to the 3'-UTR region of DNMT1, as predicted by the program Microcosm.
B. DNMT1 is directly or indirectly regulated in SLE CD4+ T cells and it triggers the over-expression of autoimmune-associated methylation-sensitive genes involved in SLE. In normal human T cells, gene hypermethylation controlled by DNMT1 blocks the transcription activity of RNA pol II, thus silencing autoimmune-related methylation-sensitive genes such as CD70, LFA-1(CD11a) and EGFL7. In SLE CD4+ T cells, promoter hypomethylation allows binding of transcriptional factors (TF) and recruiting of RNA pol II (step 1). This leads to the overexpression of autoimmune-related genes, including EGFL7 (step 2). Interestingly, miR-126 is encoded in the 7th intron of EGFL7. Thus the expression of EGFL7 leads to elevated levels of miR-126, which downregulates the production of DNMT1 in a reciprocal negative feedback (amplification) loop (step 3). Low level of DNMT1 leads to the hypomethylation status which maintains the aberrant autoimmune response (step 4). Other miRNAs contributing to decreased DNMT1 activity are miR-148a, through direct inhibition, and miR-21 which indirectly regulates DNMT1, by targeting RASGRP1 in the Ras-MAPK pathway, and thus also influencing DNMT1 protein levels.
DNMT1=DNA methyltransferase 1; TF= transcription factor; RNA pol II= RNA polymerase II; RASGRP1= RAS guanyl-releasing protein 1; bp= base pairs.