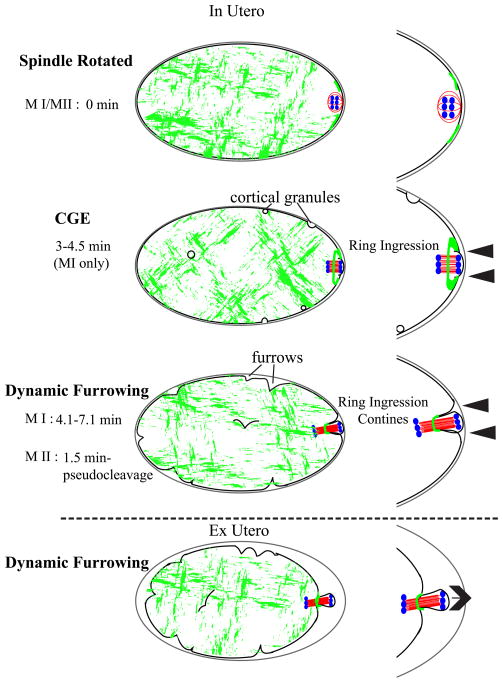
Figure 7. Global contraction model for polar body formation.
After APC/C activation, the spindle rotates to contact the cortex pole-first. There is an actomyosin ring on the surface of the embryo with a more flexible actomyosin-free center through which the spindle is pushed. Force is generated by global actomyosin contractility and the spindle midzone confers specificity of scission of the actomyosin contractile ring. In utero, it appears that the contractile ring is moving inward along the spindle (arrowheads), while in hyperosmotic conditions ex utero, the polar body appears to be pushed out (arrow) while the ring remains stationary. Grey-eggshell, black-membrane/cortex, red-microtubules, green-myosin, blue-chromosomes.